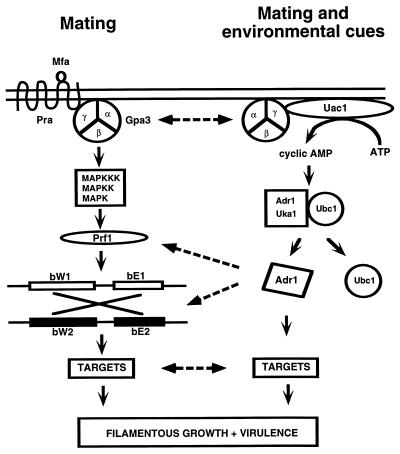
Figure 6.
Two signal transduction pathways for mating, morphogenesis, and virulence in U. maydis. The pheromone response pathway on the left shows pheromone (Mfa) binding to a receptor (Pra), activation of a postulated MAP kinase module via a heterotrimeric G protein, and activation of the transcription factor Prf1. This factor increases transcription of the b genes encoding homeodomain transcription factors (bW1, bE1, bW2, bE2; ref. 34). The cAMP signal transduction pathway is shown on the right. The major PKA catalytic subunit Adr1 may phosphorylate potential target proteins or a proposed cAMP responsive transcription factor to influence target gene transcription. Dashed arrows indicate potential interconnections of the two pathways as described in Results and Discussion.