Abstract
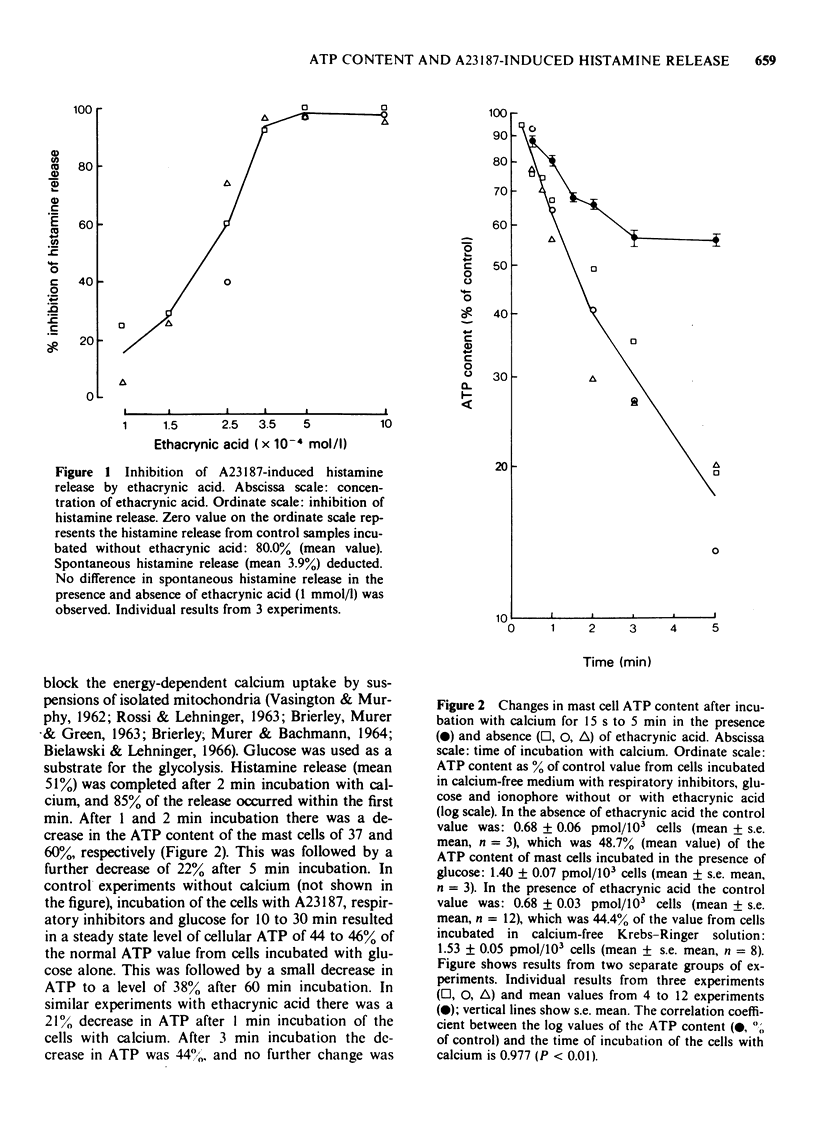
1 The relation between A23187-induced histamine release and the energy metabolism of the rat mast cells has been studied. 2 Ethacrynic acid was used as an inhibitor of calcium-induced histamine release from mast cells primed with the ionophore A23187, and to study calcium-induced changes in the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) content and the rate of lactate production of A23187-primed mast cells. 3 Ethacrynic acid by itself decreased the rate of glycolytic ATP production. 4 By measurement of the ATP content and the lactate production of mast cells with or without secretory activity, the increased demand of energy for exocytosis was estimated to be equivalent to 0.14 pmol of ATP pr 10(3) mast cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRIERLEY G. P., MURER E., BACHMANN E. STUDIES ON ION TRANSPORT. III. THE ACCUMULATION OF CALCIUM AND INORGANIC PHOSPHATE BY HEART MITOCHONDRIA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Apr;105:89–102. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90239-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIERLEY G. P., MURER E., GREEN D. E. Participation of an intermediate of oxidative phosphorylation in ion accumulation by mitochondria. Science. 1963 Apr 5;140(3562):60–62. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3562.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielawski J., Lehninger A. L. Stoichiometric relationships in mitochondrial accumulation of calcium and phosphate supported by hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4316–4322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J. C., Mongar J. L., Gomperts B. D. Calcium ionophores and movement of calcium ions following the physiological stimulus to a secretory process. Nature. 1973 Oct 5;245(5423):249–251. doi: 10.1038/245249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen T., Chakravarty N. The utilization of adenosine triphosphate in rat mast cells during histamine release induced by anaphylactic reaction and compound 48/80. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1975;288(2-3):243–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00500530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen T. Mechanism of histamine release from rat mast cells induced by the ionophore A23187: effects of calcium and temperature. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Aug;63(4):643–649. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb17277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen T. Utilization of adenosine triphosphate in rat mast cells during histamine release induced by the ionophore A23187. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;65(1):103–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb17338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSSI C. S., LEHNINGER A. L. STOICHIOMETRIC RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN ACCUMULATION OF IONS BY MITOCHONDRIA AND THE ENERGY-COUPLING SITES IN THE RESPIRATORY CHAIN. Biochem Z. 1963;338:698–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORE P. A., BURKHALTER A., COHN V. H., Jr A method for the fluorometric assay of histamine in tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Nov;127:182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svendstrup F., Chakravarty N. Glucose metabolism in rat mast cells during histamine release. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Apr;106(1):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASINGTON F. D., MURPHY J. V. Ca ion uptake by rat kidney mitochondria and its dependence on respiration and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2670–2677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


