Abstract
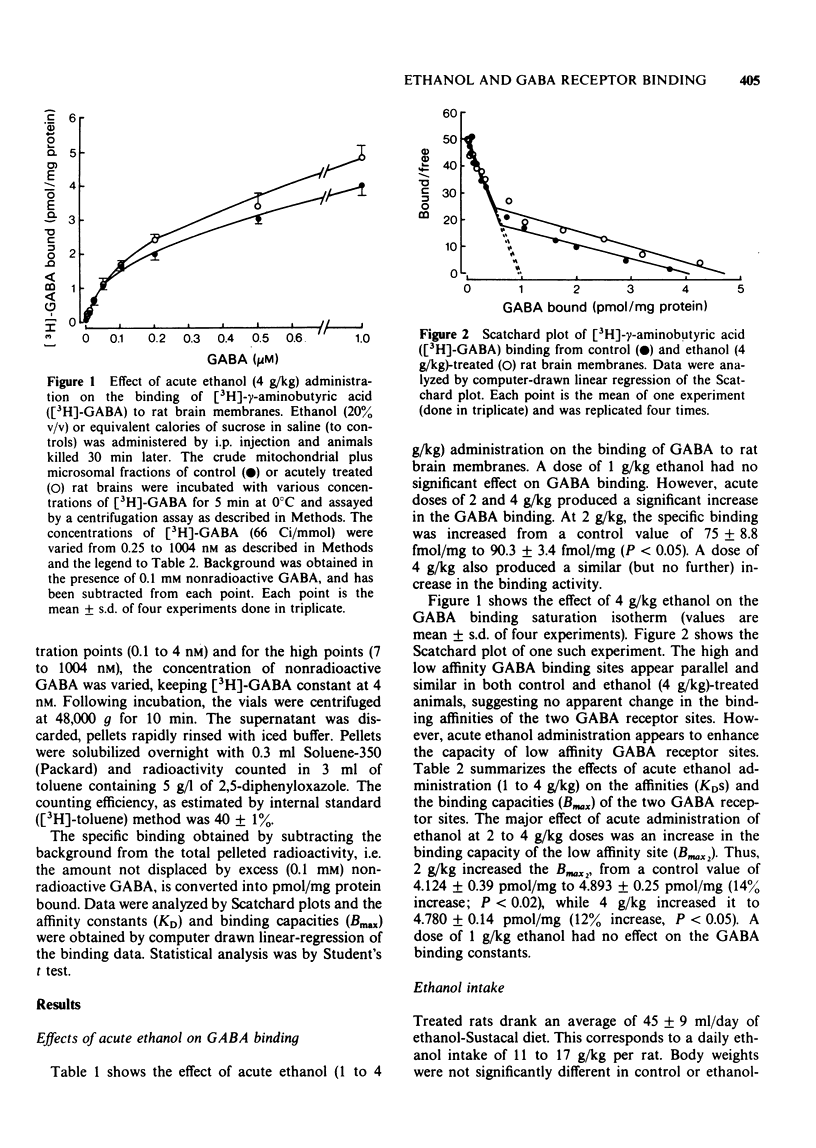
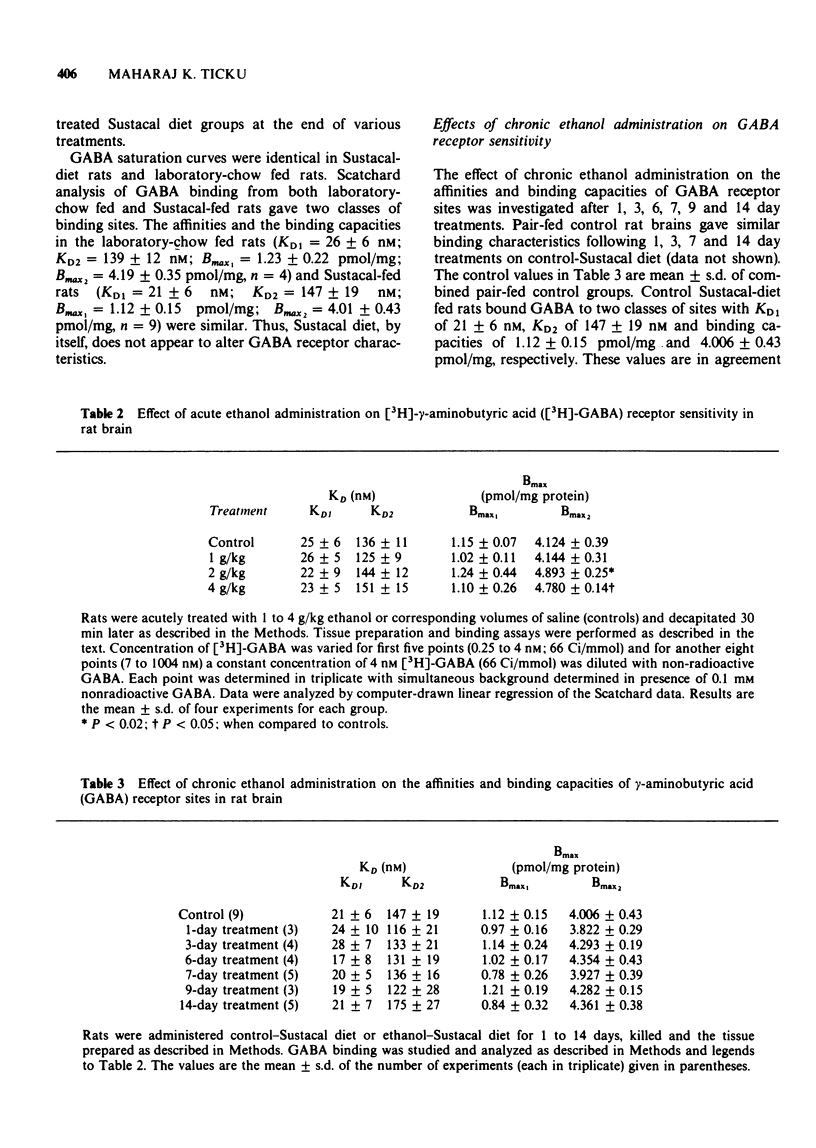
1 The effects of acute and chronic ethanol administration, and withdrawal on the binding of the inhibitory neurotransmitter, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), was investigated in rat brain. 2 Acute ethanol (2 to 4 g/kg i.p. 30 min before removal of brain) produced an increase in the binding capacity of the low affinity GABA receptor binding site. 3 Following chronic ethanol administration (1 to 21 days), the GABA receptor binding characteristics were not altered. These results suggest a possible adaptation of GABA receptors to the continuous presence of ethanol at the GABA synapse. 4 During ethanol withdrawal, the affinity of the low affinity GABA receptor binding site was significantly lower than pair-fed controls at 8 and 16 h withdrawal. 5 These results suggest that GABA receptor sensitivity may play a role in some of the neuropharmacological effects of ethanol and in its withdrawal symptoms.
Full text
PDF

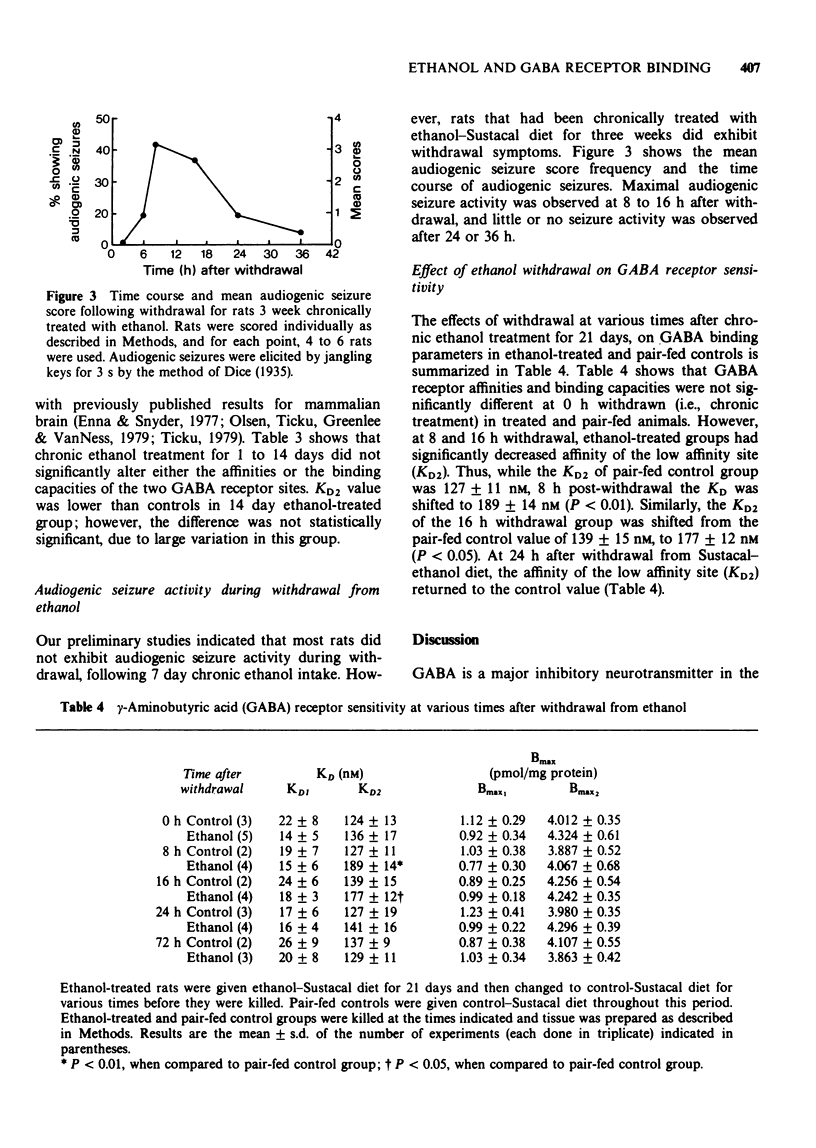



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee S. P., Sharma V. K., Khanna J. M. Alterations in beta-adrenergic receptor binding during ethanol withdrawal. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):407–409. doi: 10.1038/276407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banna N. R. Potentiation of cutaneous inhibition by alcohol. Experientia. 1969 Jun 15;25(6):619–620. doi: 10.1007/BF01896549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas B., Carlsson A. The effect of intracerebroventricularly administered GABA on brain monoamine metabolism. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;299(1):41–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00508635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Dray A. Reversal of the action of amino acid antagonists by barbiturates and other hypnotic drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 May;63(1):197–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07790.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Guidotti A., Toffano G. Molecular mechanisms mediating the action of diazepam on GABA receptors. Br J Psychiatry. 1978 Sep;133:239–248. doi: 10.1192/bjp.133.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cott J., Carlsson A., Engel J., Lindqvist M. Suppression of ethanol-induced locomotor stimulation by GABA-like drugs. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976 Dec;295(3):203–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00505087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Johnston G. A. Amino acid transmitters in the mammalian central nervous system. Ergeb Physiol. 1974;69(0):97–188. doi: 10.1007/3-540-06498-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A. Alcohol and presynaptic inhibition in an isolated spinal cord preparation. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jan;28(1):60–63. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490190078011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Influences ions, enzymes, and detergents on gamma-aminobutyric acid-receptor binding in synaptic membranes of rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 May;13(3):442–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Properties of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor binding in rat brain synaptic membrane fractions. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 12;100(1):81–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. B. Alcohol withdrawal reactions in mice: effects of drugs that modify neurotransmission. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Jul;186(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee D. V., Van Ness P. C., Olsen R. W. Endogenous inhibitor of GABA binding in mammalian brain. Life Sci. 1978 May 8;22(18):1653–1662. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakkinen H. M., Kulonen E. Ethanol intoxication and gamma-aminobutyric acid. J Neurochem. 1976 Aug;27(2):631–633. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb12295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. W., Bangham A. D. General depressant drug dependency : a biophysical hypothesis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1975;59:1–9. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0632-1_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Bloom F. E. Studies of the uptake of 3 H-gaba and ( 3 H)glycine in slices and homogenates of rat brain and spinal cord by electron microscopic autoradiography. Brain Res. 1972 Jun 8;41(1):131–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90621-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalant H. Direct effects of ethanol on the nervous system. Fed Proc. 1975 Sep;34(10):1930–1941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitch G. J., Backes D. J., Siegman F. S., Guthrie G. D. Possible role of GABA in the development of tolerance to alcohol. Experientia. 1977 Apr 15;33(4):496–498. doi: 10.1007/BF01922232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis E. K., Mulvaney M. J., Freed W. J. Effects of acute and chronic ethanol intake on synaptosomal glutamate binding activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(12):1685–1691. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90179-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyahara J. T., Esplin D. W., Zablocka B. Differential effects of depressant drugs on presynaptic inhibition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Oct;154(1):119–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A. Pentobarbital: action on frog motoneurons. Brain Res. 1975 Oct 10;96(1):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90582-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Ticku M. K., Van Ness P. C., Greenlee D. Effects of drugs on gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors, uptake, release and synthesis in vitro. Brain Res. 1978 Jan 13;139(2):277–294. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90929-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polc P., Möhler H., Haefely W. The effect of diazepam on spinal cord activities: possible sites and mechanisms of action. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;284(4):319–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00504702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom B. R., Barker J. L. Pentobarbital selectively enhances GABA-mediated post-synaptic inhibition in tissue cultured mouse spinal neurons. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 24;114(3):530–535. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90977-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzmann R. F., Tabakoff B. Body temperature in mice: a quantitative measure of alcohol tolerance and physical dependence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Oct;199(1):158–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. The membrane actions of anesthetics and tranquilizers. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Dec;24(4):583–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton U., Simmonds M. A. Effects of acute and chronic ethanol on the gamma-amino-butyric acid system in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Jul 15;22(14):1685–1692. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90381-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabakoff B., Hoffman P. L. Alterations in receptors controlling dopamine synthesis after chronic ethanol ingestion. J Neurochem. 1978 Nov;31(5):1223–1229. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb06246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K., Ban M., Olsen R. W. Binding of [3H]alpha-dihydropicrotoxinin, a gamma-aminobutyric acid synaptic antagonist, to rat brain membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 May;14(3):391–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K. Differences in gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor sensitivity in inbred strains of mice. J Neurochem. 1979 Nov;33(5):1135–1138. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K., Olsen R. W. Cage convulsants inhibit picrotoxinin binding. Neuropharmacology. 1979 Mar;18(3):315–318. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(79)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K., Olsen R. W. Interaction of barbiturates with dihydropicrotoxinin binding sites related to the GABA receptor-ionophore system. Life Sci. 1978 May 8;22(18):1643–1651. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticku M. K., Van Ness P. C., Haycock J. W., Levy W. B., Olsen R. W. Dihydropicrotoxinin binding sites in rat brain: comparison to GABA receptors. Brain Res. 1978 Jul 21;150(3):642–647. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90830-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toffano G., Guidotti A., Costa E. Purification of an endogenous protein inhibitor of the high affinity binding of gamma-aminobutyric acid to synaptic membranes of rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4024–4028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor M. The alcohol withdrawal syndrome: theory and practice. Postgrad Med. 1970 Apr;47(4):68–72. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1970.11697437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid binding to receptor sites in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4802–4807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


