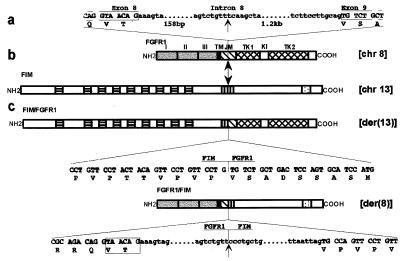
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the two partner genes and their fusion products. Vertical arrows indicate breakpoints in the FGFR1 and FIM proteins. (a) Nucleotide sequence of the junctions between exon 8 and intron 8, intron 8 and exon 9 (left and right ends, respectively), and of the breakpoint in intron 8 are indicated. (b) Schematic diagrams of the normal human FGFR1 and FIM proteins. FGFR1: three extracellular Ig-like domains (labeled I, II, and III), transmembrane domain (TM), intracellular region comprising juxtamembrane domain (JM), tyrosine kinase 1 and 2 subdomains (TK1, TK2) interrupted by a kinase insert (KI), and C-tail; FIM: N-terminal region with nine cysteine-rich motifs (▤), hydrophobic stretch rich in proline residues (▥), and a C-terminal putative bipartite nuclear localization signal (░⃞). (c) Schematic representation of the two resulting chimeric proteins. The nucleotide and deduced aa sequences near the breakpoints are shown below each protein. Portions of intronic nucleotide sequence corresponding to the FGFR1/FIM fusion gene are also shown. The boxed 6-bp sequence corresponds to the two FGFR1 variants. Upper- and lowercase letters correspond to exon and intron sequences, respectively. The chromosome position of genes encoding the four proteins is indicated on the right.