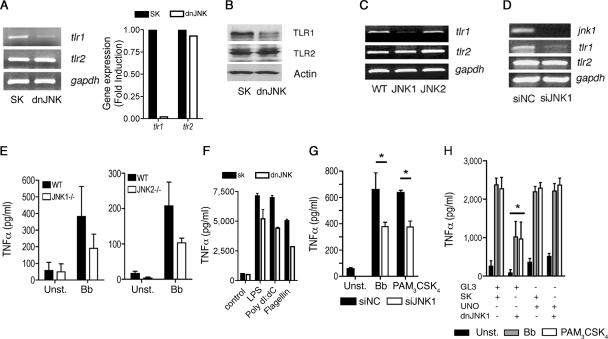
FIG. 3.
JNK1 regulates the expression of the tlr1 gene. (A) (Left) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with a plasmid containing a dnJNK form or a plasmid control (SK), and total RNA was extracted and assessed by RT-PCR (left) or real-time RT-PCR (right) for the expression of tlr1 and tlr2 mRNAs. Equal input of RNA (left) was assessed by the amplification of the housekeeping gene gapdh. (B) The cells were also used to determine the levels of TLR1 and TLR2 by Western blotting. Protein input was assessed by immunobloting with an anti-actin Ab. (C) CD11b+ cells were purified from B6 (WT) and JNK1- and JNK2-deficient mice. RNA was extracted and subjected to RT-PCR for the expression of tlr1 and tlr2. RNA input was assessed by the amplification of gapdh mRNA. (D) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with JNK1 siRNA or a control (siNC) and used to extract RNA and to determine the mRNA levels of jnk1, tlr1, and tlr2. Equal input was determined by amplification of gapdh mRNA. (E) Purified CD11b+ cells from B6 (WT) and JNK1- and JNK2-deficient mice were unstimulated (Unst.) or stimulated with a B. burgdorferi lysate (Bb). The levels of TNF-α were determined in the stimulation supernatants after 16 h. (F) dnJNK1-transfected RAW264.7 cells were stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), poly(dI-dC), and flagellin, and TNF-α was detected 16 h later. (G) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with siRNA oligonucleotides specific for JNK1 or control oligonucleotides (siNC). Forty-eight hours later, the cells were stimulated for 16 h with a B. burgdorferi lysate (Bb) or PAM3-CSK4 and assessed for TNF-α by ELISA. The results represent the average plus standard error (SE) of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05. (H) RAW264.7 cells were cotransfected with a plasmid encoding TLR1 under the influence of a constitutively expressed promoter (UNO) or a control plasmid (GL3) plus a plasmid containing the dnJNK form or the empty plasmid (SK). All cells were transfected with the same amount of plasmid. The cells were then stimulated with a B. burgdorferi lysate (Bb) or PAM3CysK4. TNF-α levels in the supernatants were determined 16 h after stimulation. The results shown represent the average plus SE of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 compared to control-, UNO plus control-, or UNO plus dnJNK-transfected cells stimulated with B. burgdorferi and PAM3-CSK4.