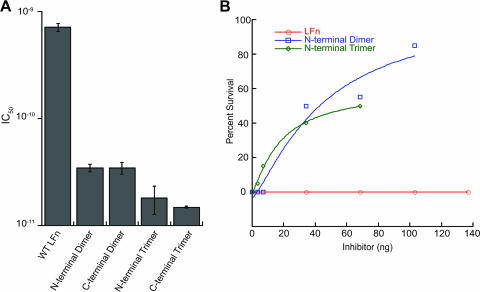
FIG. 3.
Multimeric LFN is a potent inhibitor of toxin action in cells and in zebrafish embryos. (A) CHO-K1 cells were incubated in the presence of PA, LFN-DTA, and various concentrations of inhibitor. Toxin translocation was monitored through the incorporation of [3H]leucine into newly synthesized proteins, and IC50s were calculated as described in Materials and Methods. (B) Zebrafish embryos were microinjected with PA, LFN-DTA, and various concentrations of inhibitor (n = 20 for each data point). Protection as described in the text was scored as percent embryo survival. Inhibition experiments using trimer and dimer doses of 68.5 ng were repeated two times, in which significant increases in the survival of embryos treated with each multimer were observed (trimer, P < 0.001; dimer, P < 0.001). Statistics were completed using Student's t test. WT, wild type. Error bars indicate standard deviations.