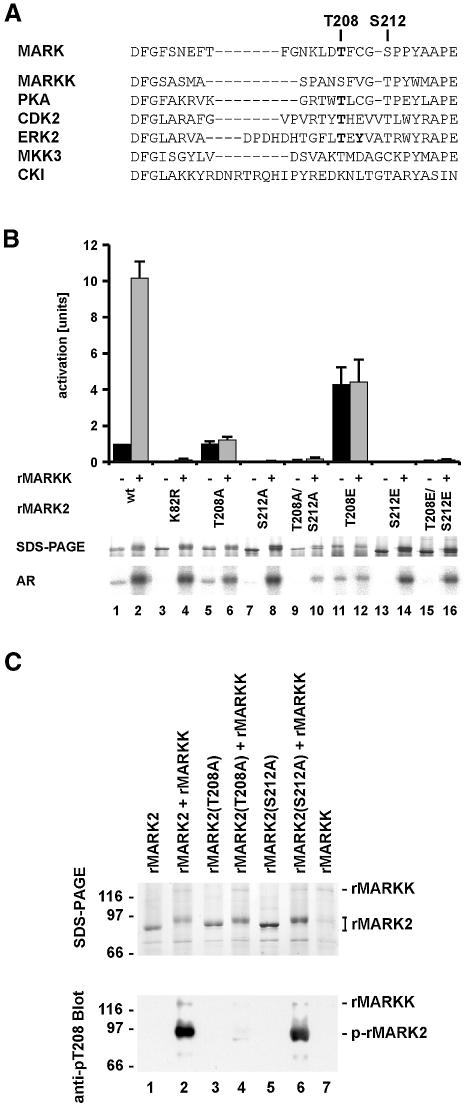
Fig. 5. Regulation of MARK. (A) Activation loop of MARK2 and other kinases. Known phosphorylation sites are in bold. (B) Influence of activation loop on MARK2 activity. Top panel, bar 1, MARK2 alone has a low basal activity of 55 nmol/min/mg. Bar 2, activation by MARKK is 10-fold. Bars 3 and 4, the K82R mutant has no activity and cannot be activated. Bars 5 and 6, the T208A mutant has the same activity as wild type, irrespective of MARKK, indicating that the phosphorylation of T208 is important for activation. Bars 7–10, the S212A mutant and the T208A/S212A mutant of MARK2 show no activity at all, indicating that S212 is important for basal activity, independently of whether T208 is phosphorylated by MARKK or not. Bars 11 and 12, the T208E mutant has a 4-fold higher activity than the wild type but cannot be activated further by MARKK. Bars 13–16, the S212E mutant and the T208E/S212E mutant of MARK2 show no activity. Middle panel, SDS gel shows the shift in Mr of all MARK2 mutants after phosphorylation with MARKK as well as the wild-type MARK2. The T208E mutant has a lower electrophoretic mobility even without phosphorylation (lane 11). Bottom panel, autoradiograms showing that autophosphorylation corresponds to activity (odd lanes). All proteins become phosphorylated upon incubation with MARKK (even lanes). This indicates at least one phosphorylation site outside the regulatory loop but with no influence on activation. (C) Phosphorylation of MARK2 and mutants (T208A or S212A) during activation by MARKK. Top, SDS gel; bottom, blot with antibody against phospho-Thr. Odd lanes without MARKK; even lanes with activation by MARKK. Lane 1, MARK2 alone. Lane 2, MARKK phosphorylates MARK2 with a shift in Mr (top), and with a prominent phospho-Thr site recognized by the pT208 antibody. Lane 3, T208A mutant of MARK2. Lane 4, MARKK causes an Mr shift of MARK2-T208A (top), but there is no phospho-Thr reaction, concomitant with the loss of activation [see (B) above]. It also shows that T208 is not responsible for the Mr shift. Lane 5, S212A mutant of MARK2. Lane 6, phosphorylation by MARKK of MARK2-S212A creates the phospho-Thr epitope at T208 (but without activity). There is an Mr shift that occurs independently of S212. Lane 7, Control, MARKK alone shows no signal with the antibody against phospho-T208.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.