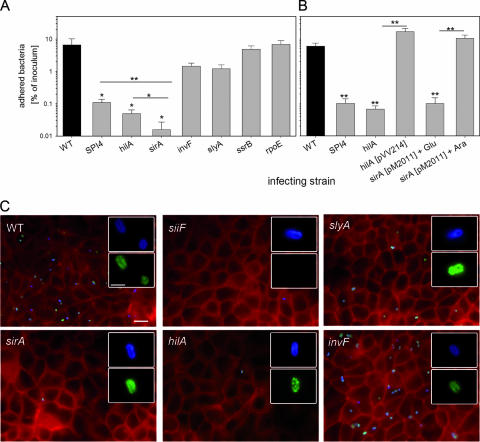
FIG. 7.
Roles of regulatory systems in the adhesion of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium to polarized epithelial cells. (A) Polarized monolayers of MDCK cells were infected with the S. enterica serovar Typhimurium WT strain and various strains defective in regulatory systems as indicated. At 25 min after the addition of the bacteria, the monolayers were washed to remove nonadherent bacteria. For the quantification of adherent bacteria, the host cells were lysed by the addition of PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100, and serial dilutions of the lysates and the inoculum were plated onto agar plates for the quantification of CFU. The mean percentages of adherent bacteria are shown with standard deviations for experiments performed in triplicate. Statistical significance was calculated by Student's t test, and * and ** indicate P values of <0.05 and <0.01, respectively. (B) Adhesion assays were performed with various strains as described for panel A. Mutant strains defective in hilA or sirA were complemented with plasmids constitutively expressing hilA or expressing sirA under the control of the araC promoter, respectively. (C) Infection of MDCK cells grown on glass coverslips with various strains was performed as described for panel A. After 25 min of infection, the cells were fixed and subjected to immunostaining for SiiE (green) and Salmonella LPS antigen O4 (blue). Subsequently, the cells were permeabilized, and the host cell F actin was stained using Texas Red phalloidin (red). The micrographs show representative overviews of the apical sides of host cells, and the insets show individual adherent bacteria at higher magnification. The scale bar represents 10 μm and 2 μm for overviews and insets, respectively.