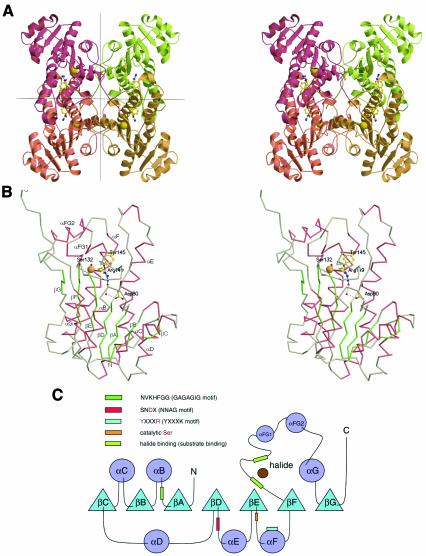
Fig. 2. (A) Stereo view of the tetrameric structure of the HheC·Br– complex. Tight dimer interactions are formed by two pairs of helices that form a four-helix bundle in the central horizontal plane. Two dimers associate by packing along the vertical plane to form the final tetramer. The location of the active site in each monomer is indicated by the catalytic serine, tyrosine and arginine in ball-and-stick representation, and the bound bromide ion as a yellow sphere. (B) Stereo view of the Cα trace of a monomer of the HheC·Br– complex. The catalytic residues Ser132, Tyr145, Arg149, Asp80 and two internal water molecules are depicted in ball-and-stick representation. The bromide ion is shown as a yellow sphere. The hydrogen-bonding pattern that extends from the catalytic base tyrosine to Asp80 at the surface of the molecule is shown as black dashed lines. (C) Secondary structure topology diagram showing the location of the sequence motifs that are responsible for halide binding, substrate binding and proton relay. The corresponding sequence motifs of the SDR enzyme family are shown in parentheses.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.