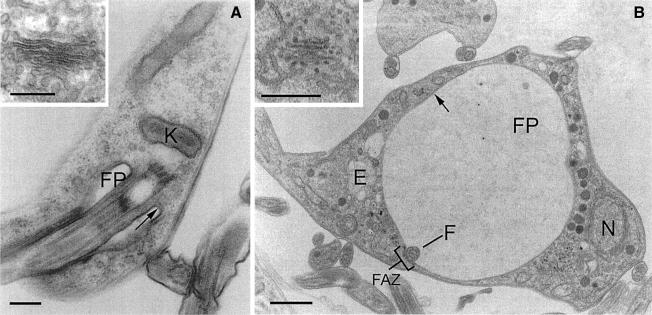
Fig. 2. BigEye is due to flagellar pocket enlargement. (A) Parental cells. The flagellar pocket is comparatively small, with a diameter of ∼0.5 µm and a flask shape due to tight association with the flagellum. (B) Induced clathrin RNAi cells. The flagellar pocket is enlarged. Other structures, including acidocalcisomes, the nucleus and endosomal membranous structures appear normal. Note also the presence of electron-dense material on either side of the flagellum where it contacts the pocket membrane, suggesting the structures responsible for flagellum/flagellar pocket association are still present in this cell. In both (A) and (B), the inset shows a Golgi complex. For both the parental and induced cell lines, the Golgi profile appears normal. E, endosome; F, flagellum; FP, flagellar pocket; FAZ, flagellar attachment zone; K, kinetoplast; N, nucleus. Arrows indicate the electron-dense variant surface glycoprotein (VSG) coat of the flagellar pocket. Scale bars: (A and A inset) 200 nm, (B) 1 µm and (B inset) 500 nm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.