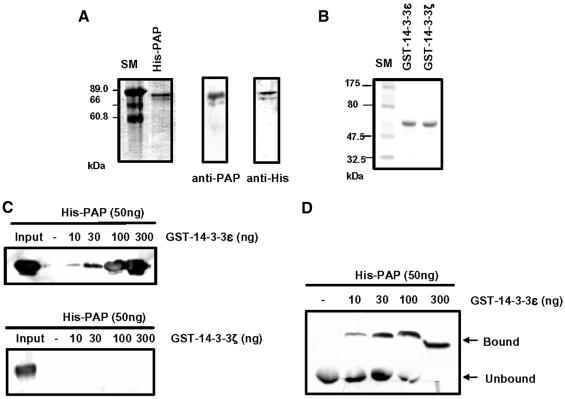
Fig. 2. Interaction of poly(A) polymerase (PAP) with 14-3-3ε in vitro. (A) Purification of the recombinant His-PAP from insect Sf9 cells. Left: the purified His-PAP was electrophoresed on a 10% SDS–polyacrylamide gel and visualized with Coomassie Blue. Right: the protein gel was blotted with anti-PAP or anti-His antibody. (B) Purification of the recombinant 14-3-3 proteins from E.coli. The purified proteins were electrophoresed on a 10% SDS–polyacrylamide gel and visualized with Coomassie Blue. (C and D) The recombinant His-PAP protein of 50 ng was incubated with the indicated amounts of GST–14-3-3ε in 30 µl of EBC solution. The protein mixture was pull downed with glutathione–Sepharose beads. The pull-downed proteins were resolved on a 10% SDS–polyacrylamide gel and blotted with anti-His antibody (C). GST–14-3-3ζ was used as a control protein (see Figure 4). Alternatively, complex formation between two proteins was analyzed by a gel mobility shift assay on an 8% native polyacrylamide gel. The protein gel was blotted by anti-His antibody (D).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.