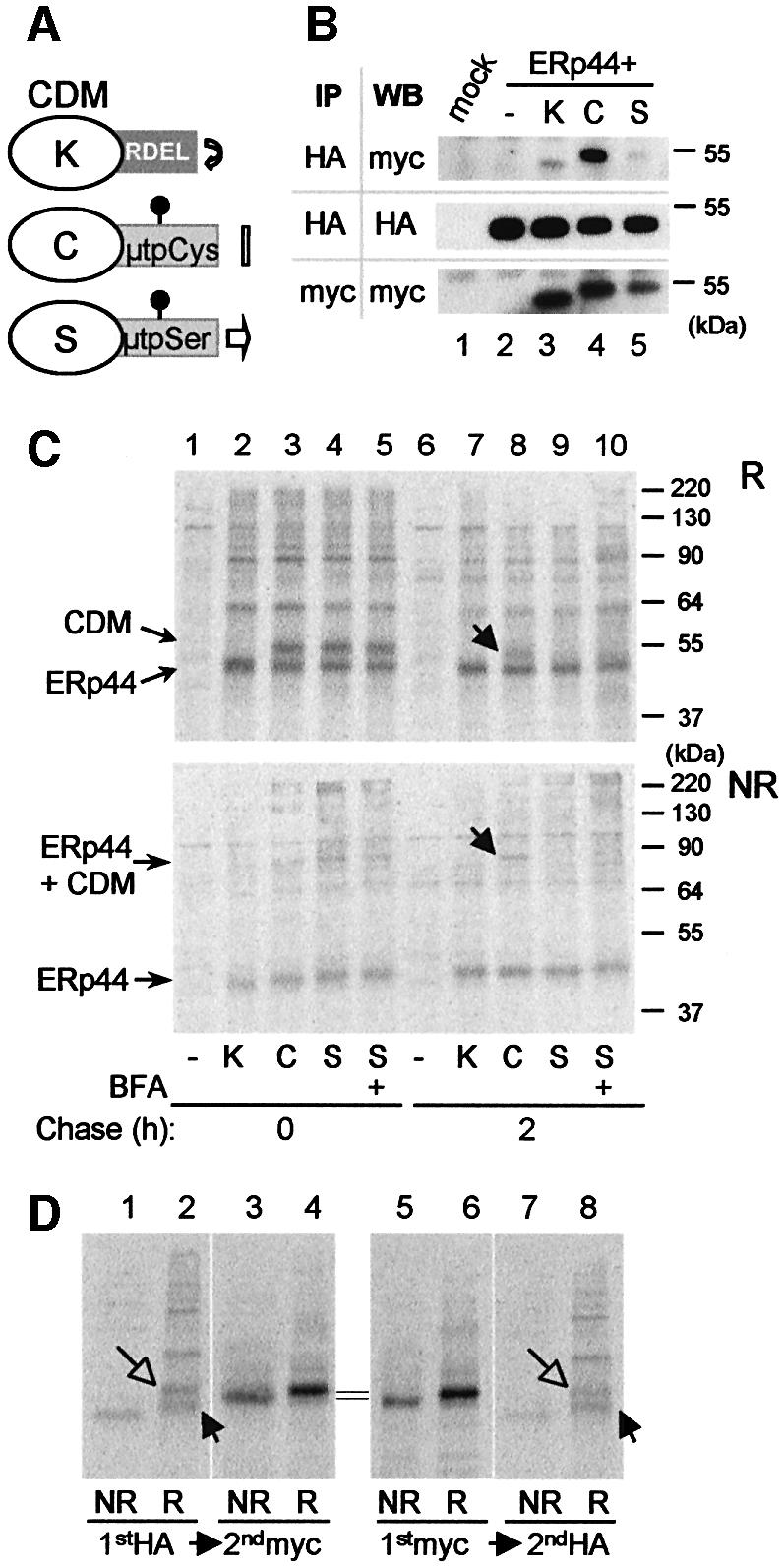
Fig. 6. ERp44 binds to C575 in the µtp. (A) Scheme of the cathepsin D chimeras utilized (Fra et al., 1993; Pelham and Munro, 1993; Isidoro et al., 1996). C-terminally myc-tagged cathepsin D constructs were further extended with SEKDEL (K) or the 20 residue µtp with a cysteine (C) or a serine (S) in the penultimate position (Fra et al., 1993). The µtp contains an N-glycan. As described previously, CDMµtpSer is transported to the Golgi and in part secreted, while CDMK and CDMtpCys are localized in the ER, the former because of its KDEL-dependent retrieval and the latter because of thiol-mediated retention. Only CDMK accumulates intracellularly with phosphorylated glycans (Isidoro et al., 1996). (B) Interaction between ERp44 and CDM chimeras at steady state. Lysates of 1 × 106 HeLa cells transfected with the vector alone (mock), or with HA-ERp44 alone or with different CDM chimeras were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HA or with anti-myc, as a control. The immunoprecipitated material was then resolved in SDS–PAGE under reducing conditions, and decorated with anti-myc or anti-HA antibodies, as indicated. Only a very little amount of CDMK and CDMµtpSer co-precipitated with ERp44 when compared with CDMµtpCys. Note that the µtp confers higher electrophoretic mobility to the chimeras, also owing to the presence of a glycosylation site [also see (A)]. (C) HeLa cells co- transfected with HA-ERp44 and cathepsin D chimeras as indicated were pulsed for 15 min with [35S]amino acids and chased for 0 (lanes 1–5) or 2 h (lanes 6–10) with or without BFA (1 µg/ml). The anti-HA immunoprecipitated materials obtained from cell lysates were resolved under reducing (R, top panel) or non-reducing (NR, bottom panel) conditions. While at the beginning of the chase all CDM chimeras co-precipitate with ERp44, after 2 h chase only CDMµtpCys remains covalently associated with it (lane 8, see arrows). The additional bands present in lanes 2–5 probably correspond to other HeLa endogenous proteins that associate with HA-ERp44, and are released with different kinetics (compare lanes 7–10). (D) Only a fraction of CDMµtpCys is bound to ERp44 at steady state. Lysates of HeLa cells co-transfected with HA-ERp44 and CDMµtpCys, and chased for 2 h after a 15 min pulse of radioactive aminoacids [see (B)] were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-HA or with anti-myc; the leftover of these first IPs were subsequently subjected to IP with anti-myc or anti-HA, respectively. Note that anti-myc antibodies do not co-precipitate ERp44, probably because the myc epitope is masked in the ERp44–CDM complexes. About 10% of CDMµtpCys is bound to ERp44 after 2 h of chase. Closed and open arrows indicate reduced ERp44 and CDM, respectively.
