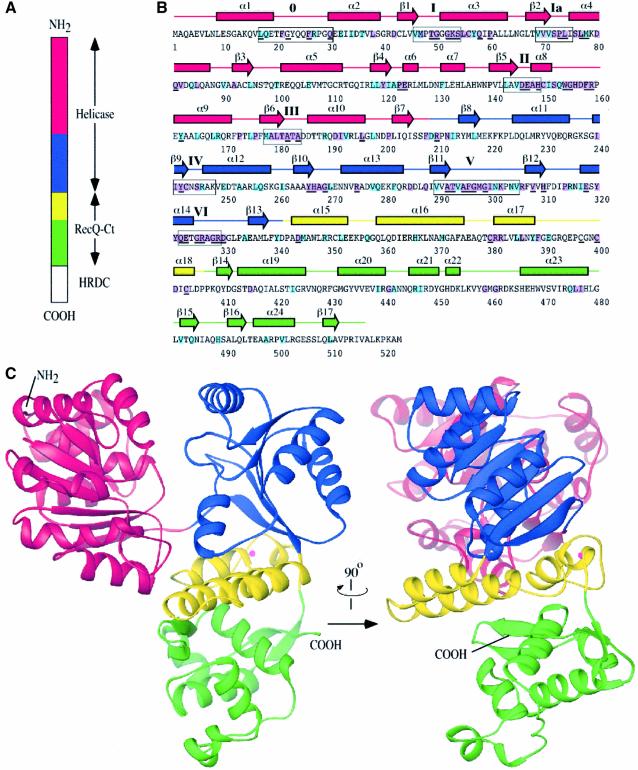
Fig. 1. Structure of the E.coli RecQ catalytic core. (A) Schematic diagram of E.coli RecQ. Three conserved regions, helicase, RecQ-conserved (RecQ-Ct), and Helicase-and-RNaseD-C-terminal (HRDC) (Morozov et al., 1997), are labeled. The catalytic core of E.coli RecQ (RecQΔC) includes only the helicase and RecQ-Ct regions, and comprises four apparent subdomains in the structure: residues 1–208 in red, 209–340 in blue, 341–406 in yellow, and 407–516 in green. (B) Sequence and secondary structure of RecQΔC. Helices (boxes) and β-strands (arrows) are shown above the sequence and labeled sequentially. Color coding is the same as in (A). Conserved helicase motifs (motif 0, Bernstein and Keck, 2003; and motifs I-VI, Gorbalenya and Koonin, 1993) are labeled and enclosed in boxes. Residues that are invariant among 65 bacterial RecQ proteins are underlined, and residues that are invariant or highly conserved with a subset of eukaryotic RecQ proteins (human WRN, BLM, and S.cerevisiae Sgs1) are highlighted in purple or light-blue boxes, respectively. (C) Orthogonal views of a ribbon diagram of the crystal structure of RecQΔC, color-coded as in (A). A bound Zn2+ ion is shown as a magenta sphere.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.