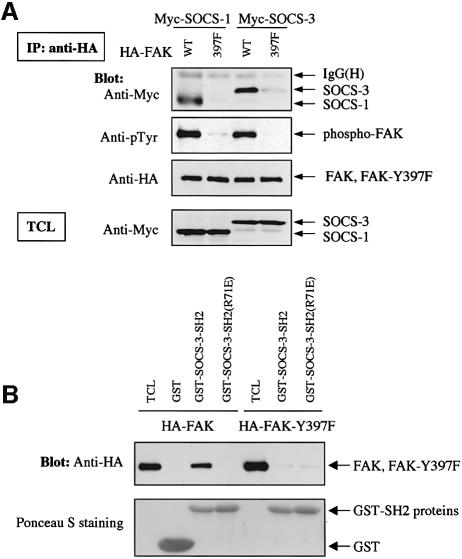
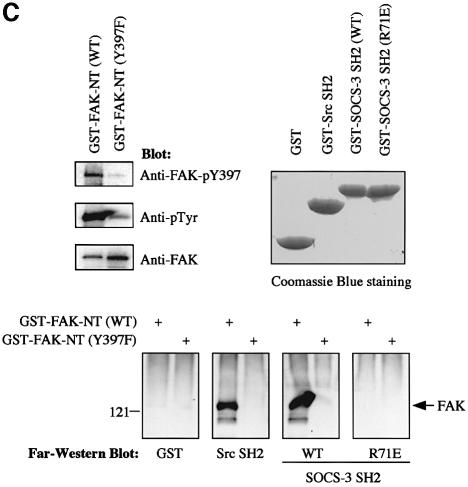
Fig. 3. Y397 in FAK regulates the FAK–SOCS interaction. (A) COS-7 cells were transiently transfected with the indicated plasmids (0.2 µg of HA-FAK or HA-FAK-Y397F, 0.5 µg of Myc-SOCS-1/3). Forty-eight hours after transfection, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody, and the precipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against Myc, pTyr or HA. Total cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-Myc antibody to confirm SOCS protein expression levels. (B) Denatured lysates of HA-FAK or HA-FAK-Y397F-transfected COS-7 cells were incubated with purified GST or with GST–SOCS-3-SH2 fusion proteins conjugated to glutathione–Sepharose beads. Associated proteins were examined by anti-HA immunoblotting (top panel). Ponceau S staining of the same blot is shown on the bottom panel. (C) GST fusion proteins coding for the N-terminal domain (amino acids 1–406) of wild-type or Y397-mutant of FAK were produced in the bacterial TK strain expressing an active tyrosine kinase. The produced proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE and transferred onto PVDF membrane and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies (upper left panel), or by far-western blotting with the indicated fusion proteins as described in Materials and methods (lower panel). Coomassie Blue staining of the fusion proteins used as probes is shown on the upper right panel.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.