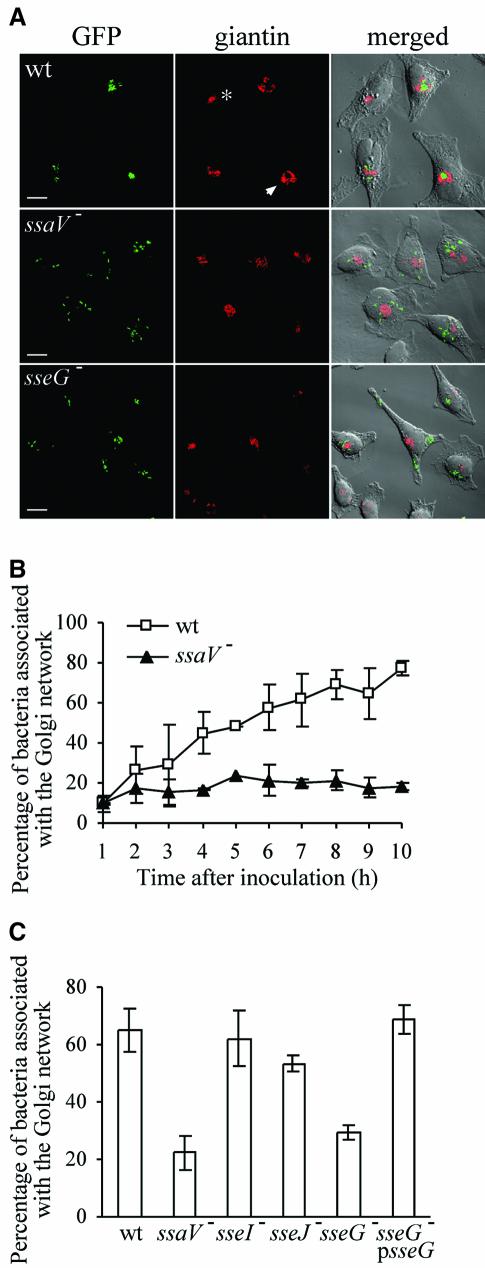
Fig. 2. Salmonella–Golgi association requires the SPI-2 TTSS effector protein SseG. (A) Intracellular distribution of GFP-expressing wild-type (wt), ssaV or sseG mutant strains in relation to giantin, 8 h after invasion of HeLa cells. Arrowhead indicates a distorted Golgi structure associated with a bacterial microcolony. Asterisk indicates compact Golgi network in an uninfected cell. Scale bars correspond to 10 µm. (B) Time course showing the increased association of wild-type S.typhimurium with the Golgi network (revealed by giantin labelling) in contrast to the ssaV mutant strain. Standard deviations from the mean are shown; results correspond to three independent experiments. (C) Association of SPI-2 effector mutant strains with the Golgi, 8 h after invasion of HeLa cells. Standard deviations from the mean are shown; results correspond to three independent experiments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.