Figure 8.
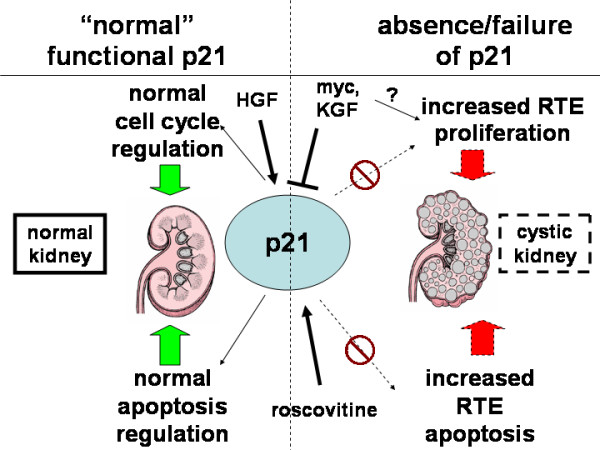
Hypothesis: attenuated or dysfunctional p21 contributes to cyst formation in ADPKD. It is likely that "normal" p21 prevents renal tubular epithelial cells (RTE) from assuming a proliferative, cystic configuration and thwarts the increased apoptosis that is seen with attenuated or maldistributed p21 which we hypothesize occurs in PKD. Myc and KGF contribute to cyst formation likely in part through p21 attenuation; roscovitine increase p21 leading to its salutary anti-proliferative effect in RTEs.
