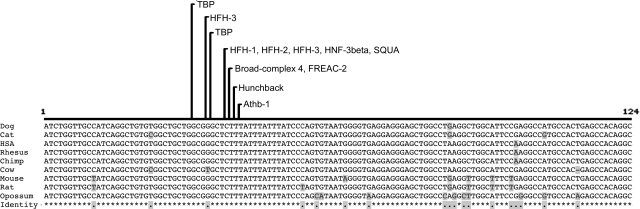
Figure 4.
Comparative alignment of the 124-bp highly conserved region within the canine cea-associated deletion for nine diverse mammalian sequences. The most strongly conserved region includes a cluster of recognition domains for several DNA-binding proteins, conserved in all nine species. These sites are listed above the alignment with lines pointing to the starting position. Locations and sequence information for these conserved binding domains are listed in Supplemental Table 6. The sequence locations for alignment are dog, chr37:28,702,470–28,702,593 rc; human, chr2:219,715,427–219,715,550 rc; chimp, chr2b:225,076,398–225,076,521 rc; rhesus, chr12:82,998,197–82,998,320 rc; mouse, chr1:74,973,801–74,973,924 rc; rat, chr9:74,386,991–74,387,114 rc; cat, scaffold_100612:247,076–247,199; cow, chr2:65,088,541–65,088,663 rc; opossum, chr7:175,293,269–175,293,392.