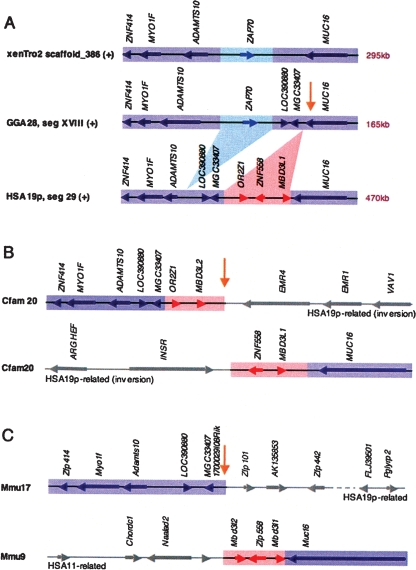
Figure 2.
Evolutionary rearrangement hotspot inside human/chicken (H/C) homology segment related to other rearrangement hotspots and H/C breakpoint reuse sites. (A) Human, chicken, and frog genomic segments between ZNF414 and MUC16 share overall gene order and orientation (purple). Respective genomic sizes are indicated and locus boundaries are accurately scaled. Gene order is interrupted at two closely spaced internal sites. First, ZAP70 (light blue) is found adjacent to ADAMTS10 in the amphibian, avian, and marsupial lineages (opossum not shown), but is in an alternate HSA2-related context in placental mammals (not shown). Second, synteny between MGC33407 and MUC16 is locally disrupted by lineage-specific gene expansions of OR2Z1, ZNF558, and MBD3L1 in human (red); it is also associated with a known duplication site (Bailey et al. 2001). (B,C). The mammalian expansion site between MGC33407 and MUC16 is reused in all other mammalian species examined. Two chromosomal locations are presented for dog (B) and mouse (C) depicting the alternate synteny contexts for each of the two homology segments flanking the reused breakpoint (yellow arrow). The human and dog rearrangement sharing the evolutionary breakpoint region near MUC16 is part of an inversion related in turn to another heavily reused evolutionary breakpoint region at INSR (see Fig. 3). The expansion associated with the opposite end of the dog inversion contains OR2Z1 and a MBD3L1 duplicate, followed by mucin-domain containing, mammalian-specific duplicates, EMR1 and EMR4. In human, the species-specific expansion at this site includes a second zinc finger ZNF557 and an expansion of MBD3L-like gene loci (Fig. 3). In mouse, the respective genomic regions flanking the breakpoint are again differentially split and rejoined, and one flank contains a different zinc finger expansion. In related H/M rearrangements mouse Emr1 and Emr4 orthologs are also split, one flanking each end of H/M segment II; one end is associated with yet another H/C reuse break while the other flank, H/M segment III, becomes a centromere proximal to mouse Insr (Supplemental Fig. S2, Supplemental Table S9).