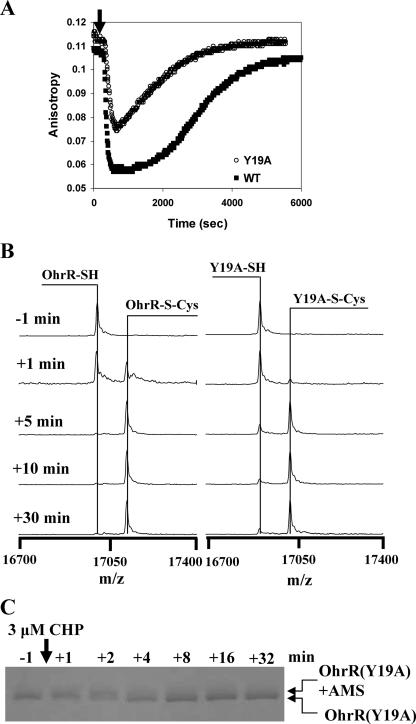
FIG. 4.
OhrR Y19A mutant has a significantly reduced rate of oxidation in vitro. (A) DNA-binding activities of WT and Y19A OhrR proteins (300 nM) determined using an FA-based assay. Addition of 300 nM CHP (in the presence of 1 mM cysteine) led to protein S cysteinylation and a decrease in the amount of protein bound to DNA. As described previously (10), the high concentration of free cysteine leads to the reactivation of OhrR by spontaneous thiol-disulfide exchange reactions. (B) Y19A OhrR protein has a reduced rate of S cysteinylation as monitored by ESI-MS. OhrR (300 nM) was treated with 3 μM CHP in the presence of 10 μM cysteine. Protein was recovered by 10% TCA precipitation and then subjected to ESI-MS. The rate of appearance of the S-cysteinylated protein was reduced ∼2- to 3-fold for the Y19A mutant, consistent with the slower and less complete inactivation shown in panel A. (C) Oxidation rate of C15 in the Y19A mutant protein as monitored by AMS modification. In this experiment, the half-time for oxidation of the C15 residue (as judged by an inability to be modified by AMS) was ∼2 min, compared to ∼30 s for WT OhrR (10; data not shown).