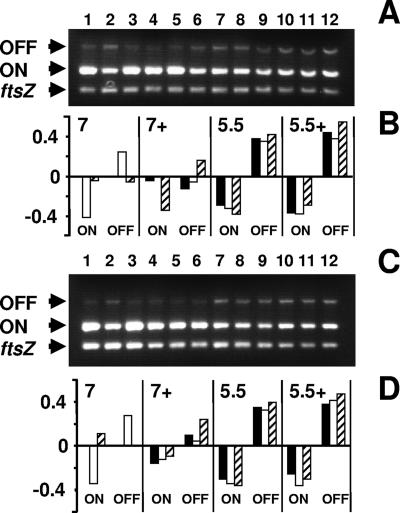
FIG. 3.
Determination of the invertible element orientation by PCR. (A) Analysis was performed on chromosomal DNA isolated from WT cells (strain AJW678), an rcsB mutant (strain AJW2143), and an rcsC mutant (strain AJW2144). Cells were harvested during mid-exponential phase following aerobic growth with 250-rpm agitation at 37°C in pH 7.0 LB medium with either no added NaCl (low salt) or 400 mM added NaCl (+; high salt) or in pH 5.5 LB medium with either no added NaCl (low salt) or 400 mM NaCl (high salt). Multiplex PCRs were set up with INV and FIMA primers to amplify “phase-on”-oriented DNA (ON; 450-bp product) (28), FIME and INV primers to amplify “phase-off”-oriented DNA (OFF, 750-bp product) (28), and EcFtsZ 1 and 2 primers to amplify the ftsZ gene (302-bp product) (27). Each multiplex was run at least three separate times. The lanes were loaded as follows: lane 1, AJW678 (pH 7.0, low salt); lane 2, AJW2143 (pH 7.0, low salt); lane 3, AJW2144 (pH 7.0, low salt); lane 4, AJW678 (pH 7.0, high salt); lane 5, AJW2143 (pH 7.0, high salt); lane 6, AJW2144 (pH 7.0, high salt); lane 7, AJW678 (pH 5.5, low salt); lane 8, AJW2143 (pH 5.5, low salt); lane 9, AJW2144 (pH 5.5, low salt); lane 10, AJW678 (pH 5.5, high salt); lane 11, AJW2143 (pH 5.5, high salt); and lane 12, AJW2144 (pH 5.5, high salt). (B) Quantification of the data from panel A. Using ImageQuant software (Molecular Dynamics), the number of pixels for each band was quantified. For each lane, the intensities of the OFF and ON states were corrected to the intensity of the ftsZ band. The corrected values for both states were standardized to the respective WT band (lane 1). Since the resultant values were plotted as log10 numbers, the WT strain for both the OFF and ON states had a value of zero, while increased and decreased PCR products resulted in positive and negative values, respectively. Solid bars, strain AJW678 (WT); open bars, strain AJW2143 (rcsB mutant); hatched bars, strain AJW2144 (rcsC mutant). (C) Analysis was performed on chromosomal DNA isolated from WT cells (strain AJW678), an rcsB mutant (strain AJW2143), and an rcsB mutant complemented with the pHRcsB plasmid (strain AJW2307) without induction. Multiplex PCR amplifications were performed with the same primer pairs, using DNAs isolated from the strains grown as described for panel A. Each multiplex was run at least three separate times. Lane 1, AJW678 (pH 7.0, low salt); lane 2, AJW2143 (pH 7.0, low salt); lane 3, AJW2307 (pH 7.0, low salt); lane 4, AJW678 (pH 7.0, high salt); lane 5, AJW2143 (pH 7.0, high salt); lane 6, AJW2307 (pH 7.0, high salt); lane 7, AJW678 (pH 5.5, low salt); lane 8, AJW2143 (pH 5.5, low salt); lane 9, AJW2307 (pH 5.5, low salt); lane 10, AJW678 (pH 5.5, high salt); lane 11, AJW2143 (pH 5.5, high salt); and lane 12, AJW 2307 (pH 5.5, high salt). All PCR products were subjected to electrophoresis on 1.5% agarose gels. (D) Quantification of the data from panel C as described for panel B. Solid bars, strain AJW678 (WT); open bars, strain AJW2143 (rcsB mutant); hatched bars, strain AJW2307 (complemented rcsB mutant).