Abstract
The kil-kor regulon of the self-transmissible, broad-host-range plasmid RK2 is a unique network with eight coregulated operons. Among the genes encoded by the kil-kor regulon are trfA, which encodes the replication initiator, and several kil loci (kilA, kilB, kilC, and kilE), each of which is lethal to the host cell in the absence of appropriate negative regulatory elements encoded by the korA, korB, korC, and korE determinants. We have proposed that the functions of the kil loci are related to RK2 maintenance or host range. Here, we report the nucleotide sequence of a 2.44-kb region that includes the lethal kilB determinant. We identified the first three genes of the kilB operon (designated klbA, klbB, and klbC), and we determined by deletion analysis that the host-lethal phenotype requires klbB. The predicted amino acid sequence of the 34,995-Da klbA product reveals a potential ATP-binding fold. The klbB product is predicted to be a membrane protein with a molecular mass of 15,012 Da with homology to the RK2 KlaC membrane protein encoded by the kilA operon. The amino acid sequence of the 12,085-Da klbC product contains a perfect match to the leucine zipper motif common to eukaryotic regulatory proteins. Primer extension analysis revealed unambiguously that transcription of the kilB operon begins 46 nucleotides upstream of klbA. No transcription was initiated from the sequence previously presumed by other investigators to be the kilB promoter. The abundance of kilB transcripts is reduced in the presence of KorB, consistent with the prediction that KorB acts at the level of transcription. A degenerate KorB-binding site that contains a perfect half-palindrome overlaps the kilB promoter, but this site is insufficient for regulation by KorB. The region containing a KorB-binding site located 183 bp upstream of the transcriptional start is required for regulation by KorB, indicating that KorB acts at a distance to regulate transcription of kilB. Our studies with the mutant plasmid pRP101, a transfer-defective derivative of the RK2-like plasmid RP4, demonstrated that the kilB operon includes the conjugal transfer and surface exclusion genes of the Tra2 region. Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed that the transposon Tn7 insertion in pRP101 is located in the klbC gene, and complementation analysis showed that this mutation has a strong polar effect on the expression of genes for conjugal transfer and surface exclusion located several kilobases downstream. A klbA mutant was constructed and found to be both transfer defective and complementable, thus, demonstrating a requirement was constructed and found to be both transfer defective and complementable, thus demonstrating a requirement for klbA product in plasmid transmissibility. These results have demonstrated a role for the kilB operon in conjugal transfer. The kil-kor regulon of RK2 is the only known example of plasmid-mediated coregulation of replication and transfer.
Full text
PDF









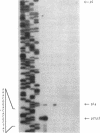
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksoy S., Squires C. L., Squires C. Translational coupling of the trpB and trpA genes in the Escherichia coli tryptophan operon. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):363–367. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.363-367.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberti S., Oehler S., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Krämer H., Müller-Hill B. Dimer-to-tetramer assembly of Lac repressor involves a leucine heptad repeat. New Biol. 1991 Jan;3(1):57–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrechtsen B., Ross B. M., Squires C., Squires C. L. Transcriptional termination sequence at the end of the Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA G operon: complex terminators and antitermination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1845–1852. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayres E. K., Saadi S., Schreiner H. C., Thomson V. J., Figurski D. H. Differentiation of lethal and nonlethal, kor-regulated functions in the kilB region of broad host-range plasmid RK2. Plasmid. 1991 Jan;25(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(91)90006-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzer D., Ziegelin G., Pansegrau W., Kruft V., Lanka E. KorB protein of promiscuous plasmid RP4 recognizes inverted sequence repetitions in regions essential for conjugative plasmid transfer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 25;20(8):1851–1858. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.8.1851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth P. T., Grinter N. J., Bradley D. E. Conjugal transfer system of plasmid RP4: analysis by transposon 7 insertion. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):43–52. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.43-52.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechhofer D. H., Figurski D. H. Map location and nucleotide sequence of korA, a key regulatory gene of promiscuous plasmid RK2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7453–7469. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechhofer D. H., Kornacki J. A., Firshein W., Figurski D. H. Gene control in broad host range plasmid RK2: expression, polypeptide product, and multiple regulatory functions of korB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):394–398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J. Superpolylinkers in cloning and expression vectors. DNA. 1989 Dec;8(10):759–777. doi: 10.1089/dna.1989.8.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkardt H. J., Riess G., Pühler A. Relationship of group P1 plasmids revealed by heteroduplex experiments: RP1, RP4, R68 and RK2 are identical. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):341–348. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Hedges R. W. Host ranges of R factors. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):453–460. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellay R., Frey J., Krisch H. Interposon mutagenesis of soil and water bacteria: a family of DNA fragments designed for in vitro insertional mutagenesis of gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fickett J. W. Recognition of protein coding regions in DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5303–5318. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Helinski D. R. Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Pohlman R. F., Bechhofer D. H., Prince A. S., Kelton C. A. Broad host range plasmid RK2 encodes multiple kil genes potentially lethal to Escherichia coli host cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1935–1939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figurski D. H., Young C., Schreiner H. C., Pohlman R. F., Bechhofer D. H., Prince A. S., D'Amico T. F. Genetic interactions of broad host-range plasmid RK2: evidence for a complex replication regulon. Basic Life Sci. 1985;30:227–241. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2447-8_19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürste J. P., Pansegrau W., Frank R., Blöcker H., Scholz P., Bagdasarian M., Lanka E. Molecular cloning of the plasmid RP4 primase region in a multi-host-range tacP expression vector. Gene. 1986;48(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90358-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlitz M., Hrabak O., Schwab H. Partitioning of broad-host-range plasmid RP4 is a complex system involving site-specific recombination. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6194–6203. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6194-6203.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo R., Nieto C., Fernandez-Tresguerres M. E., Diaz R. Bacterial zipper. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):866–866. doi: 10.1038/342866a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goncharoff P., Saadi S., Chang C. H., Saltman L. H., Figurski D. H. Structural, molecular, and genetic analysis of the kilA operon of broad-host-range plasmid RK2. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3463–3477. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3463-3477.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinter N. J., Brewster G., Barth P. T. Two mechanisms necessary for the stable inheritance of plasmid RP4. Plasmid. 1989 Nov;22(3):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann J. A., Sprague G. F., Jr Bacterial conjugative plasmids mobilize DNA transfer between bacteria and yeast. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):205–209. doi: 10.1038/340205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield V., Boyer H. W., Yanofsky C., Lovett M. A., Helinski D. R. Plasmid ColEl as a molecular vehicle for cloning and amplification of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3455–3459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagura-Burdzy G., Ibbotson J. P., Thomas C. M. The korF region of broad-host-range plasmid RK2 encodes two polypeptides with transcriptional repressor activity. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):826–833. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.826-833.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagura-Burdzy G., Khanim F., Smith C. A., Thomas C. M. Crosstalk between plasmid vegetative replication and conjugative transfer: repression of the trfA operon by trbA of broad host range plasmid RK2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):3939–3944. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.3939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagura-Burdzy G., Thomas C. M. kfrA gene of broad host range plasmid RK2 encodes a novel DNA-binding protein. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 5;225(3):651–660. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90392-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovanovic O. S., Ayres E. K., Figurski D. H. The replication initiator operon of promiscuous plasmid RK2 encodes a gene that complements an Escherichia coli mutant defective in single-stranded DNA-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4842–4846. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4842-4846.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Kolter R., Thomas C., Figurski D., Meyer R., Remaut E., Helinski D. R. Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:268–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornacki J. A., Balderes P. J., Figurski D. H. Nucleotide sequence of korB, a replication control gene of broad host-range plasmid RK2. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90307-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornacki J. A., Burlage R. S., Figurski D. H. The kil-kor regulon of broad-host-range plasmid RK2: nucleotide sequence, polypeptide product, and expression of regulatory gene korC. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3040–3050. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3040-3050.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornacki J. A., West A. H., Firshein W. Proteins encoded by the trans-acting replication and maintenance regions of broad host range plasmid RK2. Plasmid. 1984 Jan;11(1):48–57. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanka E., Barth P. T. Plasmid RP4 specifies a deoxyribonucleic acid primase involved in its conjugal transfer and maintenance. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):769–781. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.769-781.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessl M., Balzer D., Lurz R., Waters V. L., Guiney D. G., Lanka E. Dissection of IncP conjugative plasmid transfer: definition of the transfer region Tra2 by mobilization of the Tra1 region in trans. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2493–2500. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2493-2500.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessl M., Balzer D., Pansegrau W., Lanka E. Sequence similarities between the RP4 Tra2 and the Ti VirB region strongly support the conjugation model for T-DNA transfer. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20471–20480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessl M., Krishnapillai V., Schilf W. Identification and characterization of two entry exclusion genes of the promiscuous IncP plasmid R18. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 May;227(1):120–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00260716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein C., Brenner S. Unique insertion site of Tn7 in the E. coli chromosome. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):601–603. doi: 10.1038/297601a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyras D., Palombo E. A., Stanisich V. A. Characterization of a Tra 2 function of RP1 that affects growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO and surface exclusion in Escherichia coli K12. Plasmid. 1992 Mar;27(2):105–118. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(92)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck C. 'DNA Strider': a 'C' program for the fast analysis of DNA and protein sequences on the Apple Macintosh family of computers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1829–1836. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews K. S. DNA looping. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):123–136. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.123-136.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxon M. E., Wigboldus J., Brot N., Weissbach H. Structure-function studies on Escherichia coli MetR protein, a putative prokaryotic leucine zipper protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7076–7079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. J., Helinski D. R. Unidirectional replication of the P-group plasmid RK2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 6;478(1):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R., Hinds M. Multiple mechanisms for expression of incompatibility by broad-host-range plasmid RK2. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1078–1090. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1078-1090.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Kramer F. R. Structure-independent nucleotide sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2232–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motallebi-Veshareh M., Balzer D., Lanka E., Jagura-Burdzy G., Thomas C. M. Conjugative transfer functions of broad-host-range plasmid RK2 are coregulated with vegetative replication. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Apr;6(7):907–920. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01541.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motallebi-Veshareh M., Rouch D. A., Thomas C. M. A family of ATPases involved in active partitioning of diverse bacterial plasmids. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1455–1463. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Hawley D. K., Entriken R., McClure W. R. Escherichia coli promoter sequences predict in vitro RNA polymerase selectivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):789–800. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehler S., Eismann E. R., Krämer H., Müller-Hill B. The three operators of the lac operon cooperate in repression. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):973–979. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08199.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Shipley P. Host range and properties of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa R factor R1822. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):772–780. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.772-780.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Siak J. S., Gray R. H. Characteristics of PRD1, a plasmid-dependent broad host range DNA bacteriophage. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):689–699. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.689-699.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim D. S., Yanofsky C. Translational coupling during expression of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1980 Aug;95(4):785–795. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palombo E. A., Yusoff K., Stanisich V. A., Krishnapillai V., Willetts N. S. Cloning and genetic analysis of tra cistrons of the Tra 2/Tra 3 region of plasmid RP1. Plasmid. 1989 Jul;22(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkney M., Theophilus B. D., Warne S. R., Tacon W. C., Thomas C. M. Analysis of transcription from the trfA promoter of broad host range plasmid RK2 in Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas putida, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Plasmid. 1987 May;17(3):222–232. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman R. F., Figurski D. H. Conditional lethal mutants of the kilB determinant of broad host range plasmid RK2. Plasmid. 1983 Jul;10(1):82–95. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90060-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. C., Burioni R., Helinski D. R. Genetic characterization of the stabilizing functions of a region of broad-host-range plasmid RK2. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6204–6216. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6204-6216.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. C., Helinski D. R. Definition of a minimal plasmid stabilization system from the broad-host-range plasmid RK2. J Bacteriol. 1992 Dec;174(24):8119–8132. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.24.8119-8132.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. Role of eukaryotic-type functional domains found in the prokaryotic enhancer receptor factor sigma 54. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):945–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90269-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. DNA looping. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:199–223. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhauser T. J., Filutowicz M., Helinski D. R. Replication of derivatives of the broad host range plasmid RK2 in two distantly related bacteria. Plasmid. 1983 May;9(3):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhauser T. J., Helinski D. R. Regions of broad-host-range plasmid RK2 involved in replication and stable maintenance in nine species of gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):446–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.446-455.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner H. C., Bechhofer D. H., Pohlman R. F., Young C., Borden P. A., Figurski D. H. Replication control in promiscuous plasmid RK2: kil and kor functions affect expression of the essential replication gene trfA. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):228–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.228-237.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinger V., Thomas C. M. Transcription in the trfA region of broad host range plasmid RK2 is regulated by trfB and korB. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(3):523–529. doi: 10.1007/BF00341457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingler V., Thomas C. M. Analysis of the trfA region of broad host-range plasmid RK2 by transposon mutagenesis and identification of polypeptide products. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 25;175(3):229–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90346-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Shingler V., Thomas C. M. The trfA and trfB promoter regions of broad host range plasmid RK2 share common potential regulatory sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3619–3630. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Thomas C. M. Nucleotide sequence of the trfA gene of broad host-range plasmid RK2. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 25;175(3):251–262. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90347-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalker D. M., Thomas C. M., Helinski D. R. Nucleotide sequence of the region of the origin of replication of the broad host range plasmid RK2. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(1):8–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00338997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thatte V., Bradley D. E., Iyer V. N. N conjugative transfer system of plasmid pCU1. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1229–1236. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1229-1236.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theophilus B. D., Cross M. A., Smith C. A., Thomas C. M. Regulation of the trfA and trfB promoters of broad host range plasmid RK2: identification of sequences essential for regulation by trfB/korA/korD. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8129–8142. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theophilus B. D., Thomas C. M. Nucleotide sequence of the transcriptional repressor gene korB which plays a key role in regulation of the copy number of broad host range plasmid RK2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7443–7450. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M., Ibbotson J. P., Wang N. Y., Smith C. A., Tipping R., Loader N. M. Gene regulation on broad host range plasmid RK2: identification of three novel operons whose transcription is repressed by both KorA and KorC. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5345–5359. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M., Smith C. A. Incompatibility group P plasmids: genetics, evolution, and use in genetic manipulation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:77–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M., Smith C. A. The trfB region of broad host range plasmid RK2: the nucleotide sequence reveals incC and key regulatory gene trfB/korA/korD as overlapping genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4453–4469. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M., Stalker D. M., Helinski D. R. Replication and incompatibility properties of segments of the origin region of replication of the broad host range plasmid RK2. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00338996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M., Theophilus B. D., Johnston L., Jagura-Burdzy G., Schilf W., Lurz R., Lanka E. Identification of a seventh operon on plasmid RK2 regulated by the korA gene product. Gene. 1990 Apr 30;89(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarroel R., Hedges R. W., Maenhaut R., Leemans J., Engler G., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Heteroduplex analysis of P-plasmid evolution: the role of insertion and deletion of transposable elements. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;189(3):390–399. doi: 10.1007/BF00325900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter E. G., Thomas C. M., Ibbotson J. P., Taylor D. E. Transcriptional analysis, translational analysis, and sequence of the kilA-tellurite resistance region of plasmid RK2Ter. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1111–1119. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1111-1119.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Akiyoshi D. E., Regier D., Datta A., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Characterization of the virB operon from an Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5804–5814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C., Bechhofer D. H., Figurski D. H. Gene regulation in plasmid RK2: positive control by korA in the expression of korC. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):247–252. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.247-252.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C., Burlage R. S., Figurski D. H. Control of the kilA gene of the broad-host-range plasmid RK2: involvement of korA, korB, and a new gene, korE. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1315–1320. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1315-1320.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young C., Prince A. S., Figurski D. H. korA function of promiscuous plasmid RK2: an autorepressor that inhibits expression of host-lethal gene kilA and replication gene trfA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7374–7378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegelin G., Pansegrau W., Strack B., Balzer D., Kröger M., Kruft V., Lanka E. Nucleotide sequence and organization of genes flanking the transfer origin of promiscuous plasmid RP4. DNA Seq. 1991;1(5):303–327. doi: 10.3109/10425179109020786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]