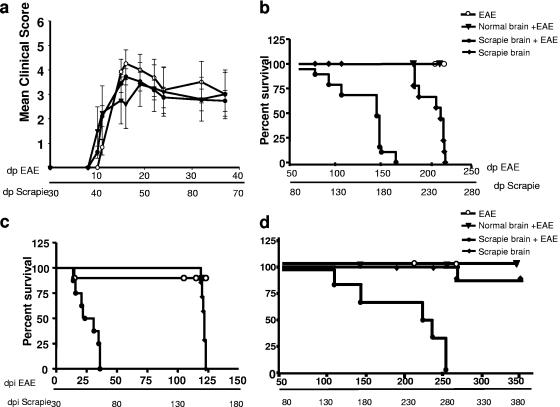
FIG. 2.
Clinical outcomes for scrapie-infected, EAE-induced, and coinduced mice. (a) EAE clinical scores. Mice induced for EAE 30 days after i.p. inoculation with saline or normal or scrapie-infected brain homogenate were scored for clinical signs as described in Materials and Methods. Each point represents the mean score ± standard deviation for all mice within the same group on the indicated days postinfection. (b) Survival time curves showing effect of i.p. (high-titer) scrapie infection. Following the acute phase of EAE, coinduced mice and scrapie-infected mice were observed for neurological signs and sacrificed when severe symptoms were apparent. The difference between both groups was highly significant (P < 0.001). (c) Survival time curves showing effect of i.c. (high-titer) scrapie infection. Mice were observed for EAE and other neurological symptoms from the day of EAE induction and sacrificed in a severe moribund state. The difference in survival times between the coinduced and scrapie-infected groups was highly significant (P < 0.001). (d) Survival time curves showing effect of i.p. (high-titer) coinduction. Following the acute phase of EAE, coinduced mice and scrapie-infected mice were observed for neurological signs and sacrificed when severe symptoms were apparent (moribund). The difference between both groups was highly significant (P < 0.001). dpi, days postinfection.