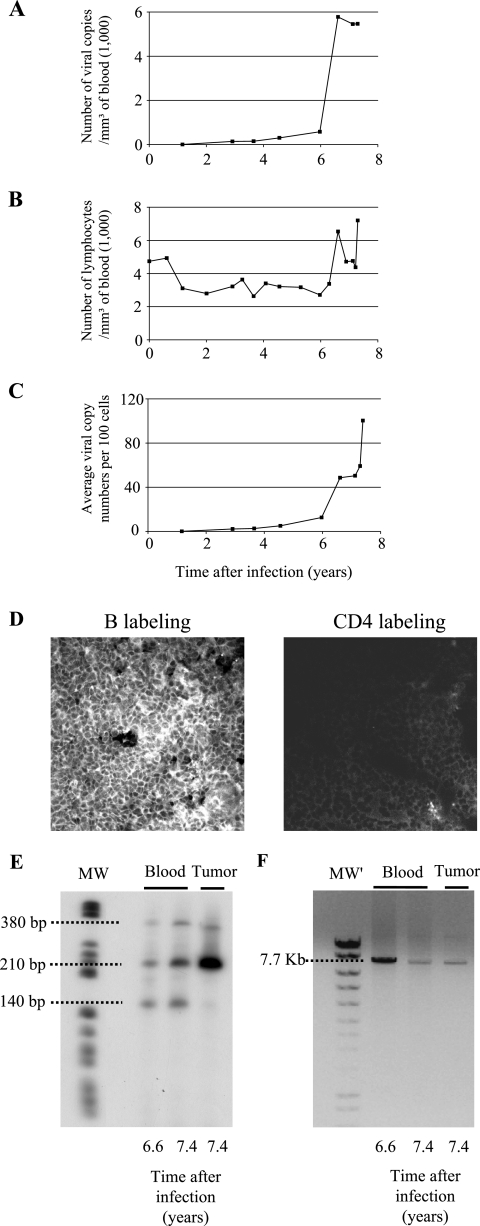
FIG. 1.
Induction of leukemia and lymphoma in sheep 245 infected with an attenuated strain of BLV harboring a deletion in the R3 and G4 accessory genes. Sheep 245 was infected with BLV provirus DX, which derives from the wild-type BLV strain 344 but contains a deletion in the R3 and G4 genes. At regular intervals postinfection, blood was collected by jugular venipuncture. (A) Proviral loads were quantified by real-time PCR and represented as numbers of viral genome copies per cubic millimeter of blood. (B) Leukocyte counts were determined by using a Coulter Counter, model ZN, and the relative proportions of lymphocytes were estimated by examination under a microscope after May-Grunwald and Giemsa staining. (C) Proviral loads reported relative to the number of peripheral blood cells. (D) Cryosections from the tumoral mesenteric lymph node were stained either with anti-CD21 (left panel) or with anti-CD4 (right panel) monoclonal antibodies in association with a fluorescein isothiocyanate conjugate and analyzed by confocal microscopy. B, B cell. (E) The profile of provirus integration sites was analyzed by inverse PCR of peripheral blood and tumor cells. The sizes of the fragments are indicated on the left. MW, molecular size markers (V; Roche). (F) DNA (250 ng) extracted from whole blood or tumor cells was subjected to nonquantitative long-PCR amplification of the integrated provirus using primers located in the 5′ and 3′ long terminal repeats (expected molecular size of the amplicon, 7.7 kb). MW′, molecular size markers (Smart Ladder; Eurogentec).