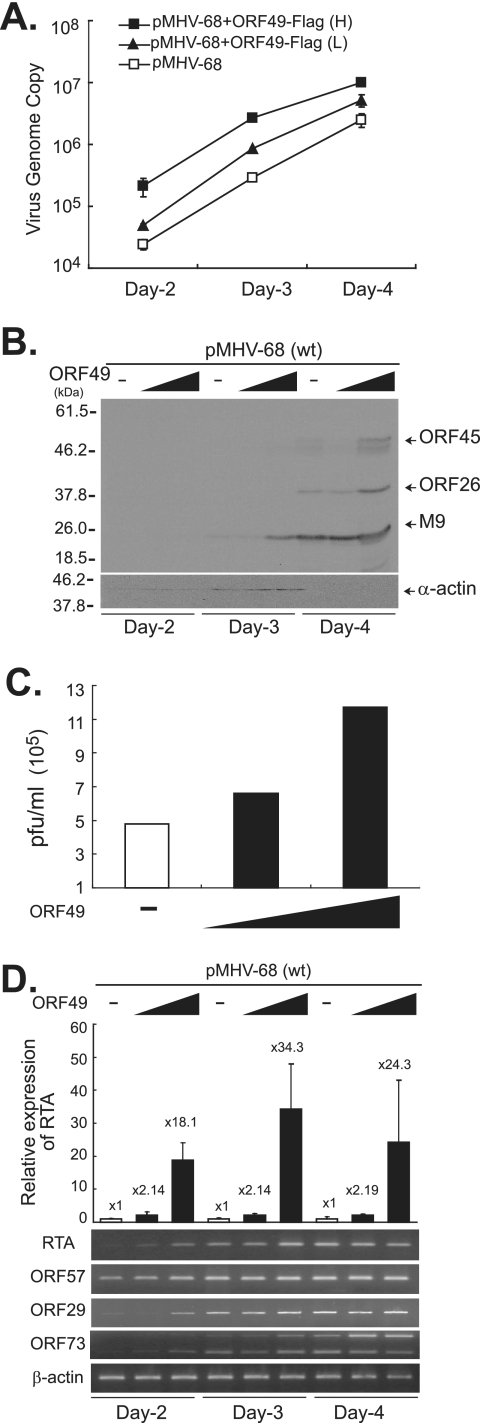
FIG. 6.
ORF49 promotes the replication of the MHV-68 virus via an increase in RTA transcription. No pFLAG-ORF49 or 100 ng (L) or 950 ng (H) of pFLAG-ORF49 was cotransfected into BHK21 cells with pMHV-68 (10 ng). The cells were harvested at 2, 3, and 4 days posttransfection. (A) FLAG-ORF49 increased viral DNA replication of the wild type (wt) in a dose-dependent manner. Total genomic DNAs were extracted and subjected to DpnI digestion prior to quantitative real-time PCR. (B) FLAG-ORF49 enhanced viral gene expression with faster kinetics. Total cellular lysates were prepared, separated on 12% gel, and subjected to Western analysis using anti-ORF45, anti-ORF26, and anti-M9 antibodies. α-Actin was utilized as a loading control. (C) Total virion production from the wild type was increased by FLAG-ORF49. Similar results were obtained from at least three independent experiments, and shown is a representative plaque assay result. (D) FLAG-ORF49 increased the levels of transcripts of RTA (immediate early), ORF57 (early), ORF29 (late), and ORF73 (latent) from wild-type MHV-68. Quantitative real-time RT-PCRs using ORF50-specific primers were conducted, and the relative ORF50 expression levels (n-fold) were calculated based on β-actin gene expression. Results are presented as the means for triplicates with their standard deviations. Another set of primers specific for the spliced transcript of RTA was utilized for RT-PCRs, and a representative gel picture is shown. The levels of ORF57, ORF29, and ORF73 transcripts were also measured via RT-PCR, and representative results are shown. β-Actin gene expression was utilized as a control.