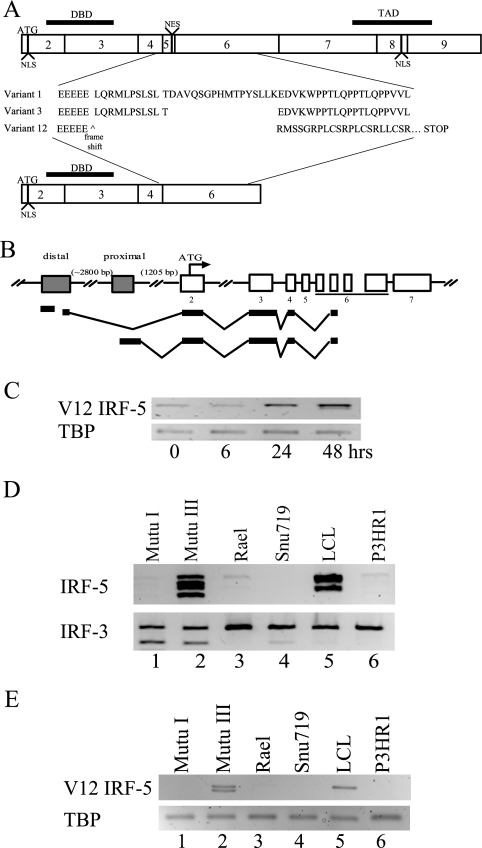
FIG. 6.
EBV infection induces a novel alternative splice variant of IRF-5, V12. (A) Exon structure of IRF-5 showing the predicted amino acid sequence of the variable exon 4 to 6 region of the V1, V3, and V12 cDNAs amplified by RT-PCR from EBV-infected cells. NLS, nuclear localization signal (3). NES, nuclear export signal (15, 44). DBD, DNA binding domain. TAD, transactivation domain. (B) Diagram of the structure of V12 cDNAs amplified by 5′ RLM RACE from Mutu III cells and cloned and sequenced. Shaded box, promoter region. (C to E) Ethidium bromide-stained, electrophoretically separated RT-PCR products amplified with primers specific for the V12 variant showing induction of V12 transcripts after EBV infection of Ramos cells (C) and expression of V12 transcripts in type III EBV-infected cell lines (Mutu III and LCL) but not in P3HR-1 or the type I latently infected B-cell lines (Mutu I, Rael) or gastric carcinoma cells (Snu719) (E). (D) Generic IRF-5 primers were used to amplify IRF-5 transcripts in the cell lines used in panel C. Amplification of cellular TBP or the ubiquitously expressed IRF-3 protein was used as a loading control. Results are representative of at least two experiments.