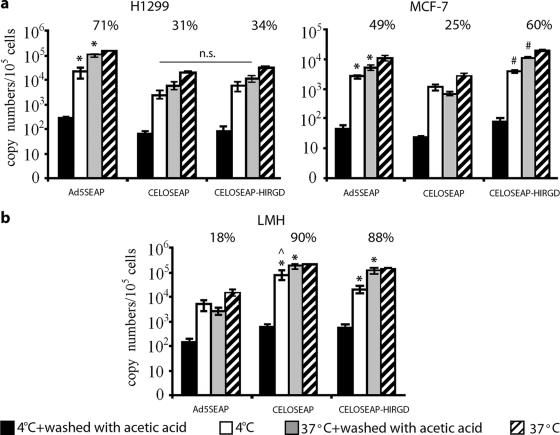
FIG. 6.
Analysis of virus internalization. (a) Binding and internalization of Ad5-SEAP and CELO vectors in CAR-positive (H1299) and CAR-negative (MCF-7) cells. *, significant difference between Ad5-SEAP and CELO vectors (P < 0.01); #, significant difference between CELO-SEAP and CELOSEAP-HIRGD (P < 0.05); n.s., statistically nonsignificant. (b) Binding and internalization of Ad5-SEAP and CELO vectors in LMH cells permissive for CELO (but not for Ad5). *, significant difference between CELO vectors and Ad5-SEAP (P < 0.005);, significant difference between CELO-SEAP and CELOSEAP-HIRGD (P < 0.05). H1299, MCF-7, and LMH cells were incubated with the indicated viruses at 1,000 vp/cell at 37°C (allowing internalization) or 4°C (allowing binding but not internalization) for 90 min. The virus was then removed, and the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). A portion of each sample was then treated with 0.2 M acetic acid to remove virus bound to the cell surface, washed with PBS, and lysed. DNA was extracted, and real-time PCR analysis of Ad5 and CELO genomic sequences was performed. The percentages of total particles that had internalized are indicated. The percentages represent the numbers of vp associated with cells (at 37°C) after the cells were washed with acetic acid divided by the total number of Ad particles that attached to the cells at the same temperature. The error bars represent standard deviations from the mean.