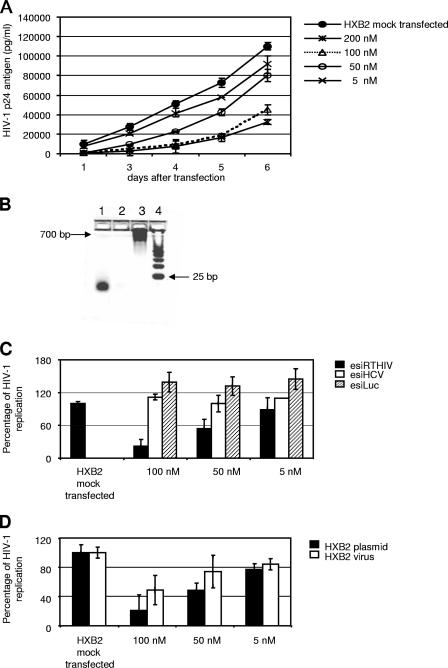
FIG. 1.
E. coli RNase III-generated esiRNAs targeting the HIV-1 RT coding region efficiently inhibit viral replication. (A) U87-CD4 cells were mock transfected or transfected with different concentrations (200, 100, 50, or 5 nM) of the esiRTHIV preparation. Cells were cotransfected with an HXB2 infectious clone. At days 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 after transfection, viral replication was monitored by determining the p24 antigen level in the culture supernatants. (B) Four percent agarose gel for determining esiRNA integrity. Line 1, 250 ng of of RNase III-digested esiRTHIV (HXB2); line 2, RNase III digestion reaction in the absence of dsRNA; line 3, 250 ng of undigested HIV-1 RT dsRNA (HXB2), line 4, size marker, 25-nucleotide DNA ladder. (C) U87-CD4 cells were mock transfected or transfected with different concentrations (100, 50, or 5 nM) of the esiRTHIV, esiHCV, and esiLuc preparations and the HXB2 infectious clone. Five days posttransfection, the supernatants of infected cells were assayed for p24 antigen levels. (D) U87-CD4 cells were mock transfected or transfected with different concentrations (100, 50, or 5 nM) of esiRTHIV. Cells were cotransfected with an HXB2 infectious clone or, alternatively, were infected 24 h after transfection with 200 50% tissue culture infectious doses of wild-type HIV-1 HXB2. Five days posttransfection or postinfection, the supernatants of infected cells were assayed for p24 antigen production. Values represent the means ± standard deviations from at least three independent experiments.