Figure 1. Complement activation in the development of CNV.
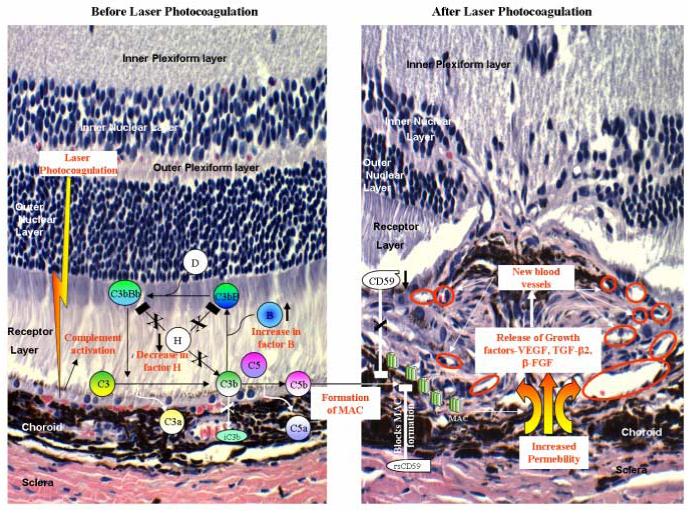
Laser photocoagulation results in up-regulation of factor B (↑) expression and decrease in (↓) factor H levels. This causes the activation and amplification of alternative pathway leading to increased deposition of MAC on the cell surface. After laser treatment the expression of CD59 is also down-regulated (↓) causing further loss of regulation (shown with X) and increased formation of MAC. Deposition of MAC results in release of growth factors such as VEGF, TGF-β2 and β-FGF, which leads to the formation of new blood vessels (shown within red circles). Administration of recombinant soluble CD59 (rs CD59) blocks (□) the formation of MAC and this results in inhibition of choroidal angiogenesis
