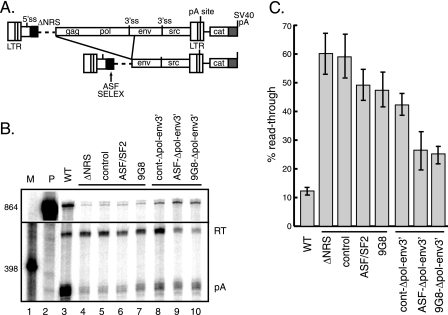
FIG. 8.
ASF/SF2 and 9G8 SELEX sites can activate RSV polyadenylation in vivo independently of the NRS-3′ ss complex. (A) Schematic of proviral constructs. Shown are the proviral long terminal repeats (LTRs); 5′ and 3′ ss; gag, pol, env, and src genes; poly(A) site; and downstream CAT gene and SVL poly(A) signal (shaded). The ASF/SF2 and 9G8 SELEX sites or control sequence (black box) replaced the entire NRS (ΔNRS; dashed line). The deletion (denoted by the lines) places the SELEX (or control) sequences nearer to the poly(A) site. (B) RNase protection assay (probe and products were the same as those used for Fig. 7) of total RNA isolated from CEFs transfected with the indicated proviral clones. Protected read-through and poly(A) products (designated on the right) were resolved on a 6% polyacrylamide gel that contains 8 M urea and visualized with a PhosphorImager. P, probe; RT, read-through RNA; pA, polyadenylated product; WT, wild type. M, 32P-end-labeled pBR322/MspI markers, the sizes of which are indicated at the left. Bands were quantitated using a PhosphorImager. (C) Quantitation of the three independent experiments.