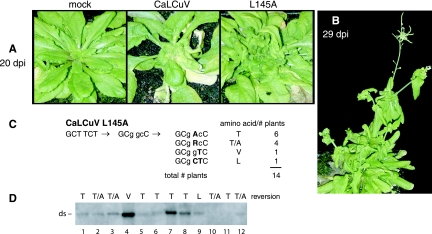
FIG. 7.
Reversion of the CaLCuV L145A mutation in Arabidopsis plants. A. thaliana plants agroinoculated with a wild-type CaLCuV B replicon and wild-type CaLCuV A or an L145A mutant replicon are shown. (A) Mock (left), wild-type (middle), and L145A (right) symptoms at 20 dpi. (B) L145A symptoms at 29 dpi. (C) The AL1 coding region between amino acids 132 and 349 was amplified from individual plants and sequenced directly. The original mutations are designated by lowercase type, and the nucleotide changes in the revertants are shown by uppercase, boldface type. The altered amino acid and the numbers of plants are shown on the right for each type of revertant. The total number of plants analyzed is indicated below. (D) Total DNA was isolated from plants at 29 dpi and analyzed by agarose gel blot hybridization. The reversion at L145A is indicated at the top of each lane. The position of double-stranded (ds) CaLCuV A DNA is marked on the left.