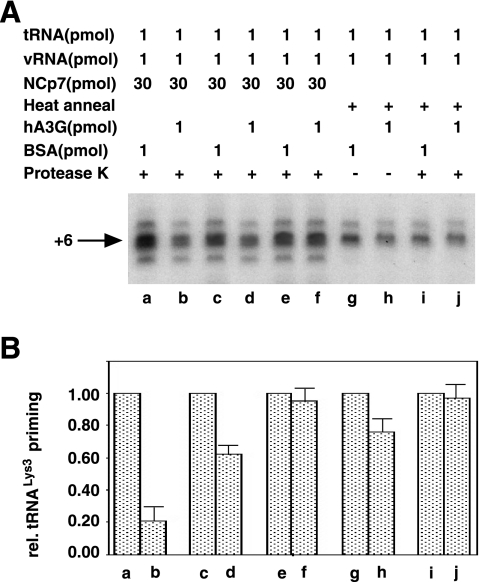
FIG. 3.
Effect of the order of addition of reactants upon tRNA3Lys priming. (A) The radioactive tRNA3Lys extended 6 bases by reverse transcription and resolved by 1D PAGE. (B) The quantitation of the gels shown in panel A, using the major middle band. Lanes a, c, e, g, and i represent reverse transcription reactions using annealed complexes (tRNA3Lys annealed to viral RNA [vRNA]) exposed to BSA during their formation, while lanes b, d, f, h, and j represent reverse transcription reactions using annealed complexes exposed to hA3G during their formation. In all cases, after reverse transcription the reaction products were deproteinized, alcohol precipitated, and resolved by 1D PAGE. Lanes: a and b, annealed complexes formed in the presence of BSA (a) or hA3G (b), deproteinized, and used in the reverse transcription reaction; c and d, annealed complex formed, deproteinized, and used in the reverse transcription reaction in the presence of either BSA (c) or hA3G (d); e and f, annealed complex formed, deproteinized, and exposed to either BSA (e) or hA3G (f) for 90 min (the annealed complex was then deproteinized and used in the reverse transcription reaction); g and h, tRNA3Lys heat annealed to viral RNA and then exposed to either BSA (g) or hA3G (h) for 90 min and used in reverse transcription reactions; i and j, tRNA3Lys heat annealed to viral RNA and then exposed to either BSA (i) or hA3G (j) for 90 min, deproteinized, and used in the reverse transcription reaction.