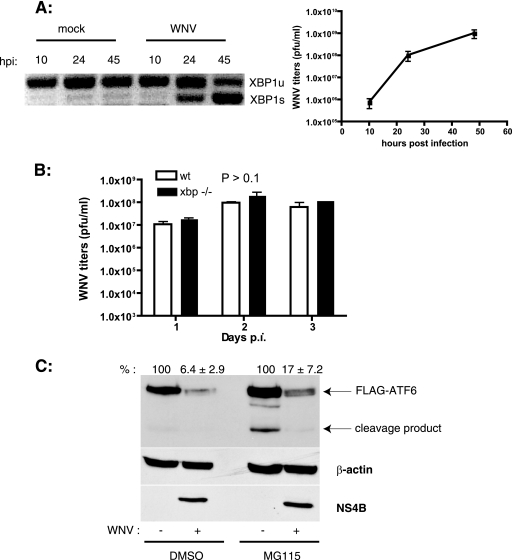
FIG. 2.
WNV infection induces xbp1 splicing and ATF6 degradation. (A) SK-N-MC cells were infected with WNV (MOI, 10), and total RNA was isolated from cells at the indicated times p.i. xbp1 splicing was analyzed by PCR as described in Materials and Methods. Unspliced (xbp1u) and spliced (xbp1s) forms are shown. WNV titers in the culture supernatants were determined by plaque assay on Vero cells. Results are representative of two independent experiments. Data are means ± standard deviations (SD). (B) Wild-type (wt) and xbp1−/− cells were infected with WNV at an MOI of 3. Supernatants were collected on the indicated days p.i., and WNV titers were determined by plaque assay on Vero cells. Three independent experiments were performed with duplicate samples. Data are means ± SD. (C) HEK293T cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing 3× FLAG-ATF6 followed by infection with WNV at an MOI of 5. At 36 h p.i., cells were treated with dimethyl sulfoxide or 50 μM MG115 for 4 h, and cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-FLAG, anti-β-actin, and anti-WNV NS4B antibodies. ATF6 expression levels (averages ± SD) from two independent experiments are indicated.