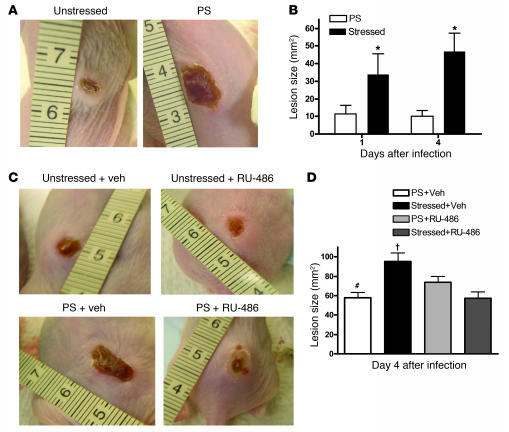
Figure 8. PS increases the severity of cutaneous GAS infection.
(A) Female 8- to 10-wk-old Skh1/Hr mice were subjected to normal conditions or PS for 72 h, and then subsequently injected intradermally with 4.8 x 108 CFU/ml GAS (n = 6 per group). Mice were then photographed daily for 4 d to monitor lesion size. (A) Representative lesions at day 4 from nonstressed and PS mice. (B) Lesion size (mean ± SEM) was calculated ± SEM for day 1 and day 4 lesions. *P < 0.05 versus nonstressed. (C) Representative lesions of PS mice (n = 5–6 per group) immediately prior to and 72 h after IP injection with either vehicle or RU-486 (6 mg/kg). After 72 h of PS or nonstressed conditions, mice were injected intradermally with 4.8 x 108 CFU/ml GAS. A representative photograph of day 4 lesions from each group is shown. (D) Lesion size (mean ± SEM) was calculated for day 4 lesions. †P < 0.05 versus PS and RU-486; #P < 0.05 versus PS and vehicle.