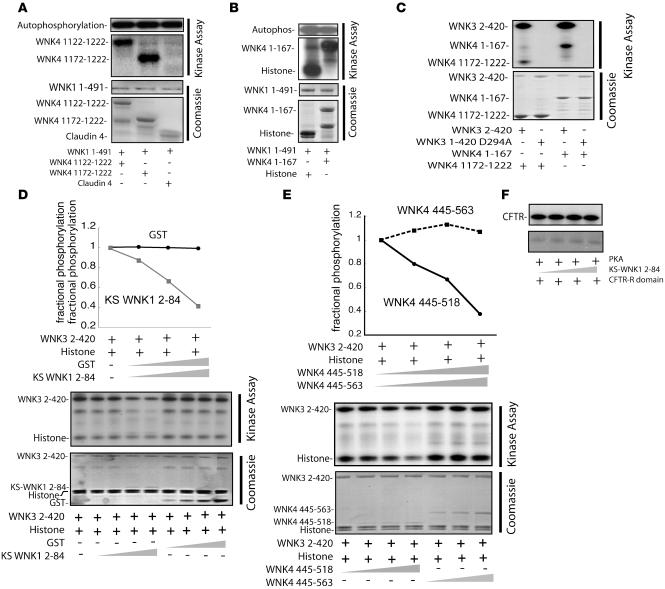
Figure 2. WNK kinase and inhibitory activity.
(A) WNK1 1–491 phosphorylated the WNK4 carboxyl terminus, but not claudin 4. (B) WNK1 1–491 phosphorylated histone and the amino-terminal domain of WNK4 (WNK4 1–167). (C) WNK3 2–420, but not WNK3 2–420 D294A, phosphorylated both the amino and carboxyl termini of WNK4. Results are representative of 5 identical experiments. (D) KS-WNK1 2–84 inhibited WNK3 kinase activity in a dose-dependent manner, whereas GST alone had no effect. Results are representative of experiments performed in triplicate. (E) GST-WNK4 445–518 inhibited WNK3 phosphorylation of itself and of histone in a dose-dependent manner. WNK4 445-563, which extends beyond the autoinhibitory domain, had no effect. Results are representative of experiments performed in triplicate. (F) KS-WNK1 2–84 did not inhibit cAMP-activated PKA activity, as detected by phosphorylation of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) R domain.