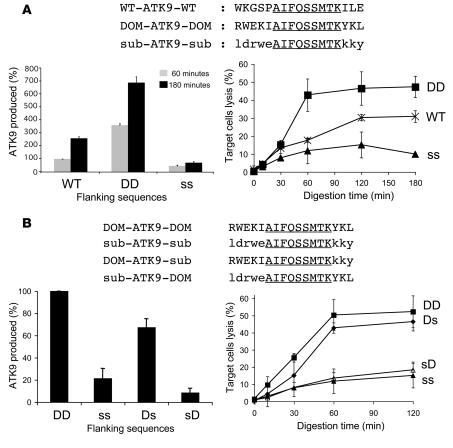
Figure 4. Identification of portable immunodominance sequences.
(A) 8 nmol of 17-mer WT-ATK9-WT or hybrid peptides DOM-ATK9-DOM and sub-ATK9-sub (where DOM and sub designate the origin [RK9 or KK9] of the flanking sequences) were incubated with 40 μg PBMC extracts for increasing periods of time (peptide sequences in top panel). The amount of ATK9 produced at time 60 (gray bars) and 180 (back bars) was analyzed by mass spectrometry and RP-HPLC (lower left panel). 100% corresponds to the amount of ATK9 produced in 1 hour during the degradation of WT-ATK9-WT. Digestion products from WT-ATK9-WT (WT, Xs), DOM-ATK9-DOM (DD, squares), or sub-ATK9-sub (ss, triangles) were used at 0.05 μg/ml to pulse 51Cr-labeled HLA-A3 B cells used as targets in a 51Cr release assay using ATK9-specific CTLs (lower right panel). (B) Similar to A except that the 4 hybrid peptides used for the digestion experiment were DOM-ATK9-DOM, sub-ATK9-sub, DOM-ATK9-sub, and sub-ATK9-DOM. 100% corresponds to the amount of ATK9 produced in 1 hour during the degradation of DOM-ATK9-DOM. Digestion products from 5R-ATK9-3R (DD, squares), sub-ATK9-sub (ss, filled triangles), DOM-ATK9-sub (Ds, diamonds) and sub-ATK9-DOM (sD, open triangles) were used at 0.05 μg/ml to pulse 51Cr-labeled HLA-A3+ B cells used as targets in a 51Cr release assay using ATK9-specific CTLs (lower right panel). Data are the average of 3 experiments performed with extracts from 3 healthy donors.