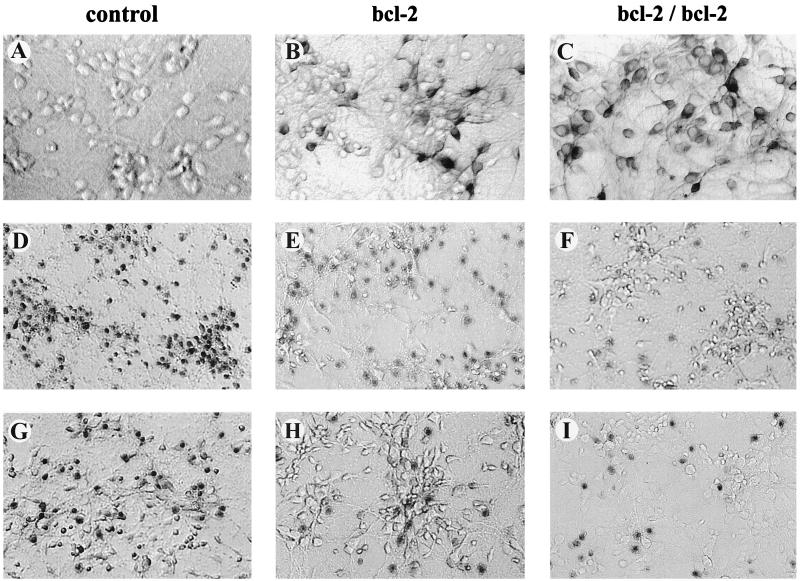
Figure 1.
Photomicrographs of the murine cortical cultures used to analyze the neurotoxicity of 6-OHDA and MPP+. Immunocytochemical staining for the hBcl-2 protein was found in both the heterozygous (B) and homozygous cultures (C), but was absent in the wild-type cultures (A). After exposure of the cultures to 6-OHDA (10–100 μM) and MPP+ (10–50 μM) for 18–24 h, cell viability was assessed by using the trypan blue exclusion procedure. Cell counts (mean ± SEM) of three random fields (1,500–2,500 cells) revealed the percentage of dead cells. Representative fields of cells treated with 30 μM 6-OHDA (D–F) and 50 μM MPP+ (G–I) are shown for wild-type (D, G), heterozygous (E, H), and homozygous (F, I) cultures overexpressing hBcl-2, respectively. (A–C, 200×; D–I, 150×). In all cases the hbcl-2 transgene conferred significant neuroprotection (P < 0.05; ANOVA) upon the cortical cultures. Further details are given in Figs. 2 and 3.