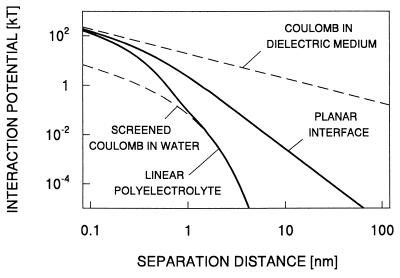
Figure 2.
Accurate numerical results for the site–site interaction potentials W(r) between two elementary charges as a function of their separation distance r in units of kT. The charges are located in a dielectric with ɛd = 3, which is in contact with aqueous electrolyte of concentration cs = 0.5 M (κ−1 ≃ 0.43 nm) and with ɛw = 80. The interface is modeled as a semi-infinite planar dielectric with charges at a depth of a = 0.25 nm from the dielectric–electrolyte interface. The polyelectrolyte is approximated by a dielectric cylinder of radius a = 0.25 nm, with charges arranged along its longitudinal axis. The limiting law for small distances is the Coulomb potential in the dielectric; for large distances the interaction potential decays like r−3. For the cylinder the large distance behavior is given by a screened Coulomb law in water.