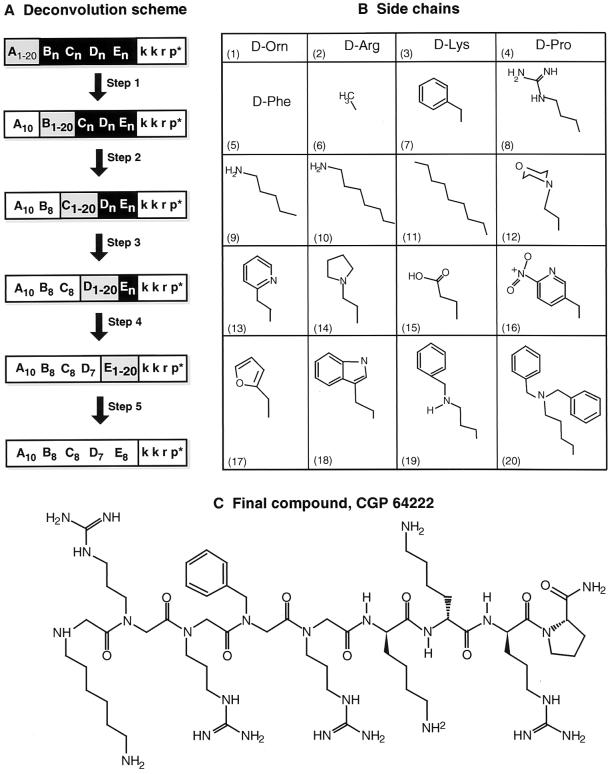
Figure 1.
(A) Scheme for the deconvolution of combinatorial libraries. Initially 20 sublibraries carrying unique residues in position A (A1–20; gray box; subscripts refer to side-chain numbers shown in B) and a random collection of side chains in positions B, C, D, and E (Xn; black box) were synthesized. k k r p* indicates d-Lys-d-Lys-d-Arg-d-Pro-amide. The sublibrary with the greatest inhibitory activity against the Tat/TAR RNA interaction was detected by using a gel mobility-shift assay. After the optimal residue for position A had been selected, another set of 20 sublibraries was prepared with a fixed residue in position A (A10, white box), unique residues at position B (B1–20; gray box), and a random collection of side chains in positions C, D, and E (Xn; black box). This deconvolution process was continued until a single compound was identified. (B) Structure of side chains used to create the combinatorial library. (C) Structure of the final compound, CGP64222.