Fig. 4.
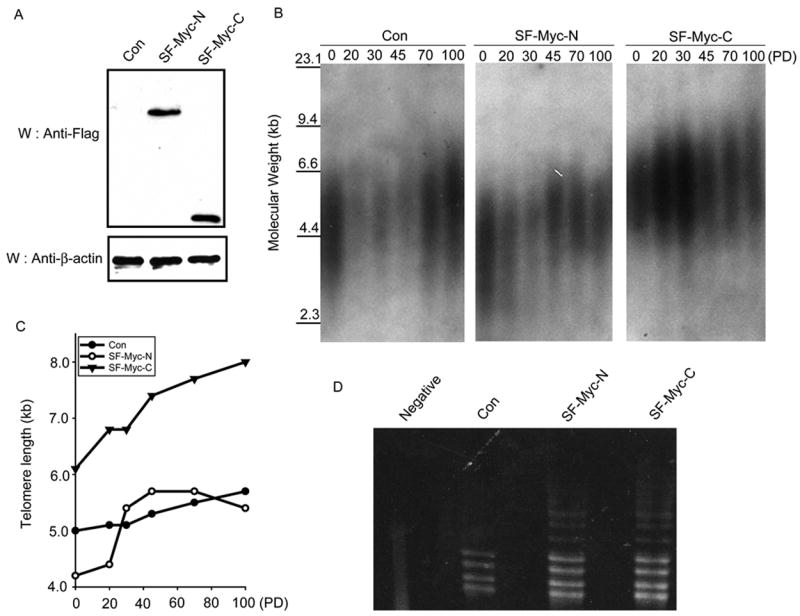
Expression of C-terminal region of c-Myc leads to an increase of telomere length. A, Establishment of HT1080 cell lines stably expressing c-Myc deletion mutants. Anti-Flag antibody was used to detect the expression levels of these c-Myc mutants. Anti-β-actin Western blot was used as a loading control. B, Telomere restriction fragment length analysis was performed using vector transfected control cell line and cell lines stably expressing c-Myc deletion mutants. These cell lines were collected at the indicated generations or population doublings. Extracted genomic DNA was digested with HinF1 and RSA1, separated on a 0.6% agarose gel and transferred to nylon-cellulose membranes. Southern blotting was performed using [32P]-ATP-labeled-(TTAGGG)4 probe. C, The mean size of telomere length was estimated using ImageQuant software and Telorun. Kb, kilobase; PD, population doublings. D, Telomerase activity in these stable cell lines was determined by TRAP assay. Heat-inactivated lysate prepared from cells stably expressing SF-Myc-C was included as a negative control (Negative).
