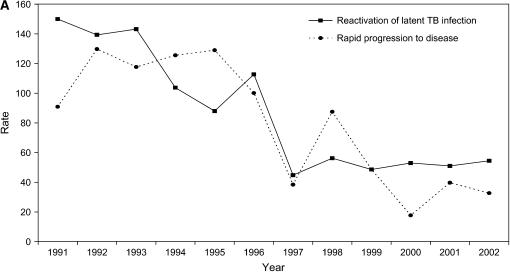
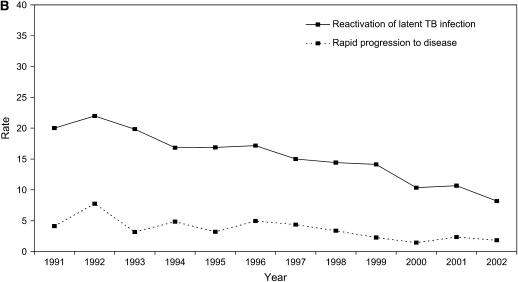
Figure 2.
Tuberculosis case rates as the number of tuberculosis cases per 100,000 population, by HIV test result. (A) Rates of HIV-positive tuberculosis cases due to reactivation of latent tuberculosis infection (solid line) versus secondary cases caused by recent transmission and rapid progression to disease (dashed line). We calculated the tuberculosis case rate among persons coinfected with HIV and Mycobacterium tuberculosis using the estimated number of HIV-positive persons in San Francisco as the denominator (San Francisco Department of Public Health, unpublished data). (B) Rates of HIV-uninfected tuberculosis cases due to reactivation of latent tuberculosis infection (solid line) versus secondary cases caused by recent transmission and rapid progression to disease (dashed line). We calculated the tuberculosis case rate among HIV-uninfected patients using the estimated number of persons living in San Francisco minus the estimated number of HIV-positive persons in San Francisco as the denominator. TB = tuberculosis.