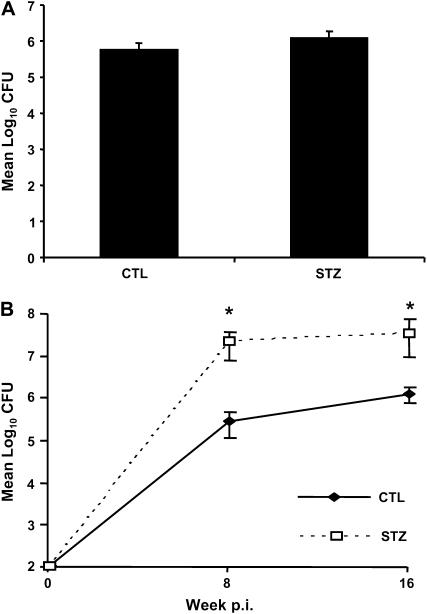
Figure 1.
Chronic but not acute diabetes increases tuberculosis (TB) susceptibility in mice. We grouped mice as acute or chronic based on the duration of streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetes, ⩽ 1 mo or ⩾ 3 mo, respectively, before aerosol infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) Erdman (∼ 50 colony-forming units [cfu]). Lung Mtb load was determined by plating serial dilutions of lung homogenates at the indicated times and counting cfu after 3 wk incubation. (A) Acute diabetic (STZ) versus euglycemic control (CTL) mice 4 weeks after infection. (B) Chronic STZ diabetic versus euglycemic mice 8 and 16 weeks after infection. Data are presented as mean log10 cfu ± SD. Open squares: STZ-treated mice with chronic diabetes; closed diamonds: euglycemic control mice. Data are presented as mean cfu ± SD. *P < 0.05, n = 5.