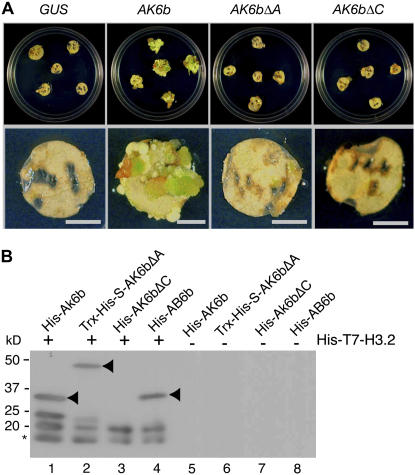
Figure 1.
Mitogenic Activity of 6b and Its Interaction with Histone H3.
(A) Callus-formation assay. DNA constructs for recombinant proteins of wild-type AK6b and mutant AK6bΔA and AK6bΔC, as described in Methods and in Supplemental Figure 1 online, were linked to the 35S promoter of Cauliflower mosaic virus, and each 6b construct and a control β-glucuronidase (GUS) gene construct were introduced into cells of tobacco leaf discs by a Ti plasmid vector system. The leaf discs were incubated on agar plates that contained selective medium without cytokinin and auxin (see Methods). Bars = 5 mm.
(B) Binding of 6b and its derivatives to histone H3.2. Recombinant His-T7-histone H3.2 protein was incubated with His-AK6b (lanes 1 and 5), Trx-His-S-AK6bΔA (lanes 2 and 6), His-AK6bΔC (lanes 3 and 7), and His-AB6b (lanes 4 and 8), and protein complexes were immunoprecipitated with T7-specific antibodies as described in the text. The recovered complexes were subjected to SDS-PAGE (10.5% acrylamide) and protein gel blot analysis with His-specific antibodies. Proteins of 6b and its derivatives are indicated by arrowheads. Some 6b protein was detected as two forms (lanes 1 and 2), one of which might have been a degradation product. His-T7-histone H3.2 was also detected as two forms. The rapidly migrating proteins, indicated by an asterisk, might also represent degradation products.