Figure 3.
SAW Proteins Affect Leaf Margin Development.
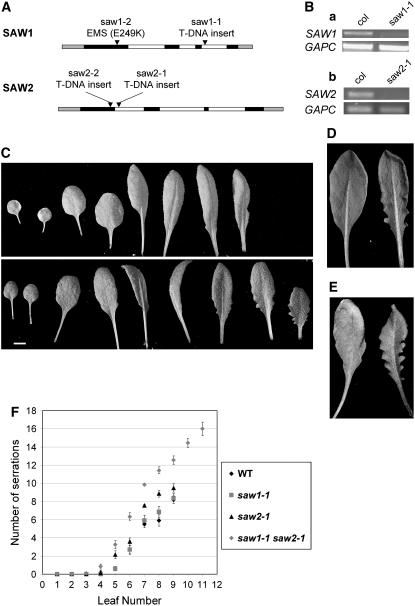
(A) Graphical representations of the transcribed regions of SAW1 and SAW2 genes. Black, white, and gray boxes indicate exons, introns, and untranslated regions, respectively. The position of mutation/insertion in each mutant allele is marked by an arrowhead.
(B) RT-PCR analysis of SAW1 and SAW2 expression in wild-type (Col) and saw mutants. The fifth and sixth leaves were harvested from 4-week-old plants for RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis. (a) SAW1 expression is considerably reduced in saw1-1 compared with the wild type. Cytosolic-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPC) was used as a loading control. SAW1, 35 cycles; GAPC, 28 cycles. (b) There is no detectable SAW2 expression in the leaves of saw2-1 mutants, but SAW2 is detected in wild-type leaves. SAW2, 35 cycles; GAPC, 25 cycles.
(C) A comparison of the leaves of 4-week-old wild-type (top) and saw1-1 saw2-1 (bottom). saw1-1 saw2-1 double mutants had more serrations than the wild type from the seventh leaf onward. The fourth leaf of the double mutant was longer and more ovate than the fourth wild-type leaf.
(D) Leaf margins of saw 1-1 saw2-1 double mutants are more revolute than wild-type leaf margins, as shown by an abaxial view of the eighth leaf of 4-week-old wild-type (left) and saw1-1 saw2-1 (right) plants.
(E) The difference in the length of leaf serrations is more pronounced in older plants, as shown by an adaxial view of the ninth leaf of five-week-old wild-type (left) and saw1-1 saw2-1 plants (right).
(F) Leaves of both saw1-1 saw2-1 double mutants and saw2-1 single mutants had more serrations than wild-type leaves. Scatterplot showing the number of serrations for each leaf of 5-week-old wild-type, saw1-1, saw2-1, and saw1-1 saw2-1 plants. Serrations were counted only on the rosette leaves that had been initiated prior to bolting. Points represent means ± se. As can be seen from the chart, saw1-1 saw2-1 double mutants also initiate more leaves than the wild type prior to bolting.