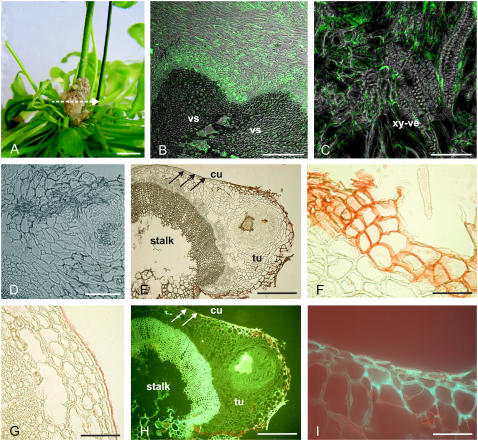
Figure 2.
Localization of suberin and ABA in tumors. A, Four-week-old tumor, induced by A. tumefaciens (strain C58) at an inflorescence stalk of Arabidopsis. The arrow indicates the section plane of the cross sections shown in B to I. B to D, ABA immunolocalization in tumor cross sections using a primary mouse hybridoma monoclonal antibody against ABA and a secondary antibody labeled with the green Alexa 488 chromophore. Images were taken with a confocal laser scanning microscope and show overlays of images taken in a confocal and differential interference contrast mode. B, Fluorescence signals were strongest around vascular tissue (vascular, vs) of the tumor/host inflorescence stalk interface. C, ABA immunofluorescence at cellular resolution in thin cytoplasmic layers of cells near the xylem vessels (xy-ve). D, Control cross section of a tumor, treated with 1% (w/v) rabbit serum and the secondary Alexa 488 antibody conjugate in the absence of the primary antibody against ABA, revealed no significant fluorescence signal. E to G, Images from bright-field microscopy. H and I, UV illuminated (488 nm) cross sections. E, Cross section of a tumor (tu) with a disrupted epidermis attached to an inflorescence stalk (stalk). The reddish color of the outer tumor cell layers marks Sudan-III-stained cells indicating suberin. Note that the stalk is covered by an intact epidermis, containing a cuticle (arrows). F, Closeup of outer cell layers from the tumor, attached to the host inflorescence stalk as shown in E with suberized cell walls (red) and of outer cell layers (G) from the host inflorescence stalk shown in E with a cuticle (red). H, Strong autofluorescence indicates aromatic compounds of lignified xylem vessels and outer cell layers of the tumor. I, Closeup of outer cell layers from the border between the tumor and inflorescence stalk shown in H. Autofluorescence marks cell walls of cells at the tumor surface but not at the surface of the stalk (H, white arrows). Bars: A, 5 mm; B, 100 μm; C, D, F, G, and I, 50 μm; E and H, 200 μm.