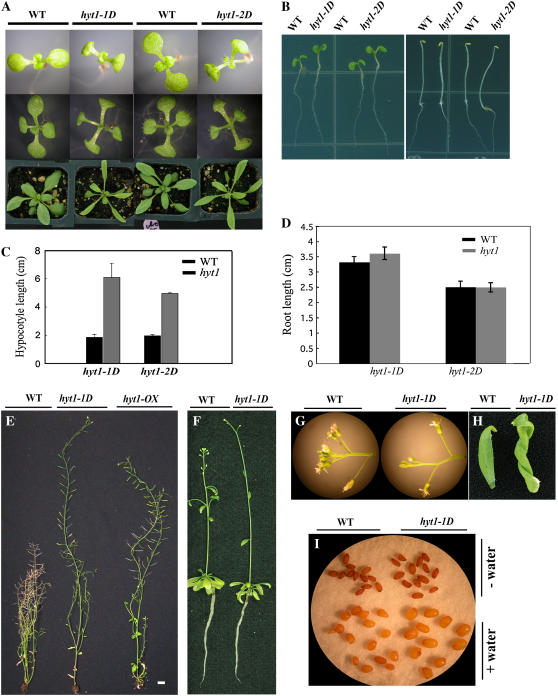
Figure 2.
Analysis of the hyt1-1D (yucca6-1D) and hyt1-2D (yucca6-2D) phenotypes. A, hyt1-1D (yucca6-1D) and hyt1-2D (yucca6-2D) plants with their wild-type plants, Col-0 gl1 and Col-0, respectively, grown for 7 d and 14 d on MS medium or 25 d on soil (from top row to bottom row). B, hyt1-1D (yucca6-1D) and hyt1-2D (yucca6-2D) plants grown on MS media for 4 d in light (left) and dark (right) conditions compared with their wild types. C, Hypocotyl length of hyt1-1D (yucca6-1D) and hyt1-2D (yucca6-2D) seedlings grown for 10 d on MS media containing 0.8% (w/v) agar compared with their wild types. Black bar is the wild type and gray bar is the mutant, n = 20. D, Root length of hyt1-1D (yucca6-1D) and hyt1-2D (yucca6-2D) seedlings grown for 7 d (yucca6-1D) and 6 d (yucca6-2D) on MS media containing 1.2% (w/v) agar compared with their wild types. Black bar is the wild type and gray bar is the mutant, n = 15. E, Six-week-old mature plants of wild type, hyt1-1D, and hyt1-OX, a transgenic plant with overexpressed transcripts of HYT1 (from left to right, respectively). Scale bar = 2 cm. F, Roots of wild-type and hyt1-1D (yucca6-1D) plants grown in hydroponic culture condition. Soil-grown 2.5-week-old seedlings were transferred to the hydroponic solution and photographed 21 d after growth in hydroponic solution. G, Flowers of wild-type (left) and the hyt1-1D (yucca6-1D) plants (right). H, Cauline leaf of 2-month-old wild-type (left) and hyt1-1D (yucca6-1D) plants (right). I, Seeds of wild type (left) and hyt1-1D (yucca6-1D; right) before (top) and after imbibing water (bottom) for 4 d.