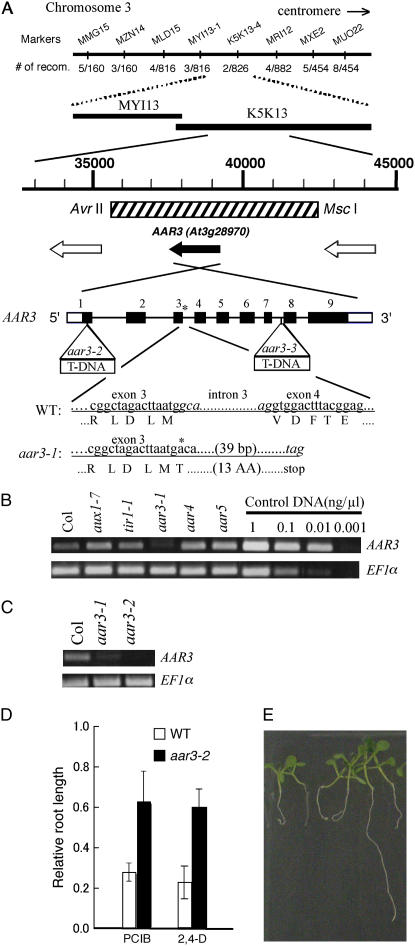
Figure 5.
Molecular cloning of the AAR3 gene. A, Fine mapping with the PCR-based markers MMG15-2, MZN14-1, MLD15-1, MYI13-1, K5K13-2, MRI12-5, MXE2-3, and MUO22-1, which are located at the MYI13 and K5K13 regions on chromosome 3. The position of the 6.6-kb DNA fragment used for the complementation test is indicated with a hatched box. Open reading frames in this region were shown with black (for AAR3) and white arrows (for other open reading frames). Black and white boxes of AAR3 indicate exons in translated and untranslated regions, respectively. Lines indicate introns. The position of the mutation in aar3-1 is indicated with an asterisk, and the positions of the T-DNA insertion in aar3-2 and aar3-3 are indicated with open triangles. aar3-1 has a G-to-A mutation at the first base of the third intron, which may prevent normal splicing and result in generation of a truncated product. Nucleotides in the third intron in the wild type and the predicted stop codon in aar3-1 are shown in italics. B and C, The steady-state levels of the AAR3 transcript in various mutants analyzed by RT-PCR. Same volume (1 μL) of control DNA with different concentration (1 ng μL−1, 0.1 ng μL−1, 0.01 ng μL−1, or 0.001 ng μL−1) was used in the PCR reaction. D, Relative root length of aar mutants grown on PCIB or 2,4-D. Seeds were germinated on GM-MES medium containing 20 μm PCIB or 40 nm 2,4-D, and grown vertically under white light for 10 d. Root growth was measured and plotted as a percentage of root growth on control medium without the growth regulators. Error bars represent sds of the means of at least 16 seedlings. E, Segregation of PCIB-sensitive seedlings in the T2 population of a transgenic aar3-2 line (line 12) transformed with the 6.6-kb fragment indicated as a hatched box in A. The seedlings were germinated and grown for 9 d on 20 μm PCIB. [See online article for color version of this figure.]