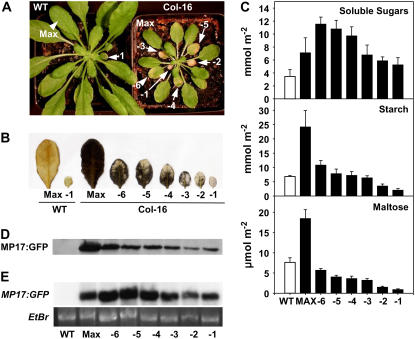
Figure 5.
Release of the MP17-induced assimilate export block in senescing leaves of high-level MP17:GFP expressing Arabidopsis plants. A, Visible phenotype of MP17:GFP expressing line Col-16 grown for 66 d under SD conditions. Fully expanded source leaf (Max) and older leaf stages with progressing leaf senescence (-6 until -1 with the latter being defined as oldest leaf within the rosette) are indicated. B, Qualitative determination of starch accumulation in different senescing leaf stages of Col-16 and wild type after an extended dark period (16 h) by iodine (KI) staining. C, Carbohydrate levels in different senescing leaf stages of Col-16 in comparison to the fully expanded source leaves of the transgenic line (Max) and wild type. Samples for determination of soluble sugar, starch, and maltose were collected at the end of the dark period of 66-d-old plants. Values are given as mean ± se of six (or five for maltose) individual plants, and soluble sugars represent the sum of Glc, Fru, and Suc. D, Western-blot analysis of MP17:GFP protein accumulation in different leaf stages of Col-16. Identical amounts of protein were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunodecorated using the polyclonal anti-MP17 antibody. E, Northern-blot analysis of MP17:GFP transcript accumulation. Each lane contains 25 μg of total RNA isolated from the indicated leaf stages of wild-type and Col-16 plants. Northern blots were hybridized with MP17 cDNA (top section) and the ethydiumbromide stain (Etbr) of the RNA gel served as loading control (bottom section).