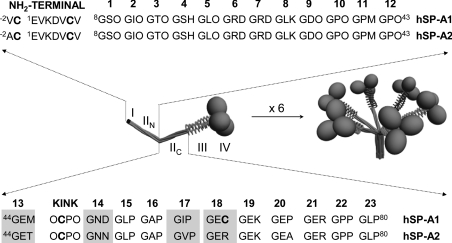
Figure 1. Three-dimensional models of trimeric (right) and oligomeric (left) forms of SP-A and sequence of the N-terminal segment and the collagen-like domain of human SP-A1 and SP-A2.
The four structural domains of the human SP-A polypeptide chain are shown: (I) N-terminal segment involved in intermolecular disulfide bond formation; (II) collagen-like domain characterized by 23 Gly-Xaa-Yaa triplets with a sequence irregularity (kink), which divides the collagen-like domain into two parts: N-terminal (IIN) and C-terminal (IIC) portions (the triplet number is shown at the top of IIN and IIC sequences); (III) neck region between the collagen and the globular domain; and (IV) C-terminal globular domain. Amino acid differences between SP-A1 and SP-A2 at residues 46, 53, 61 and 65 are shaded. Cysteine residues are shown in boldface. The letter ‘O’ represents hydroxyproline.