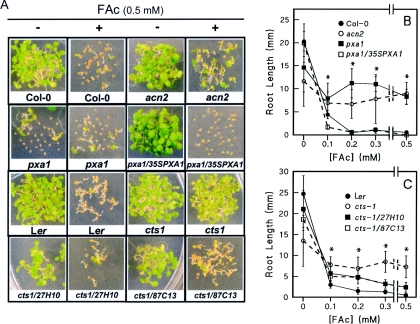
Figure 3. FAc resistance of CTS mutants.
Seeds of wild-type and complemented mutants were not nicked. The labels 27H10 and 87C13 represent clone designations from the GeTCID (Gene Transfer Clone Identification and Distribution Service) (John Innes Centre), provided for in planta expression as part of the GARNet (Genomic Arabidopsis Resource Network) facilities. pxa1/35SPXA1 represents the mutant line expressing the PXA1 cDNA under the control of the CaMV (cauliflower mosaic virus) 35S promoter [26]. (A) Seeds were treated as described in the Experimental section, except that spontaneously germinated mutants were not removed prior to nicking the testa. All seeds were sown on to standard agar medium containing 20 mM sucrose with (+) or without (−) 0.5 mM FAc. Photographs were taken 8 days after transfer to growth conditions. Root growth of Col-0-related genotypes (B) and Ler-related genotypes (C) in the presence of increasing FAc concentrations. Seeds were treated with FAc as described in the Experimental section. Root lengths were measured 6 days after nicking the testae of the mutants. Results are means±S.D. for at least ten seedlings. Lines have been included to clarify connections for obscured data points. Based on Student's t test statistics, wild-type root growth was significantly less than the mutant seedling (P<0.0001) at FAc concentrations of 0.1 mM and greater as indicated by *. Average root growth for complementation genotypes cts-1/155A23 and cts-1/159N01 was intermediate between Ler and the complementation genotypes shown.