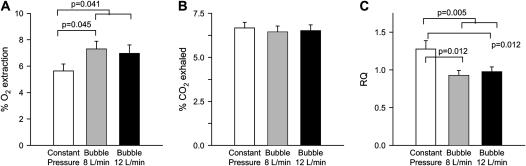
Figure 2.
Indirect calorimetry. Oxygen (O2) extraction and carbon dioxide (CO2) removal rates were calculated from the product of the breath-to-breath changes in inspired and expired O2 and CO2 and the minute volume (corrected for dry weight). Bubble continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) animals extracted O2 more efficiently than constant pressure CPAP animals (p = 0.041). The significantly higher respiratory quotient (RQ) of the constant pressure CPAP group is suggestive of respiratory failure (p = 0.005).